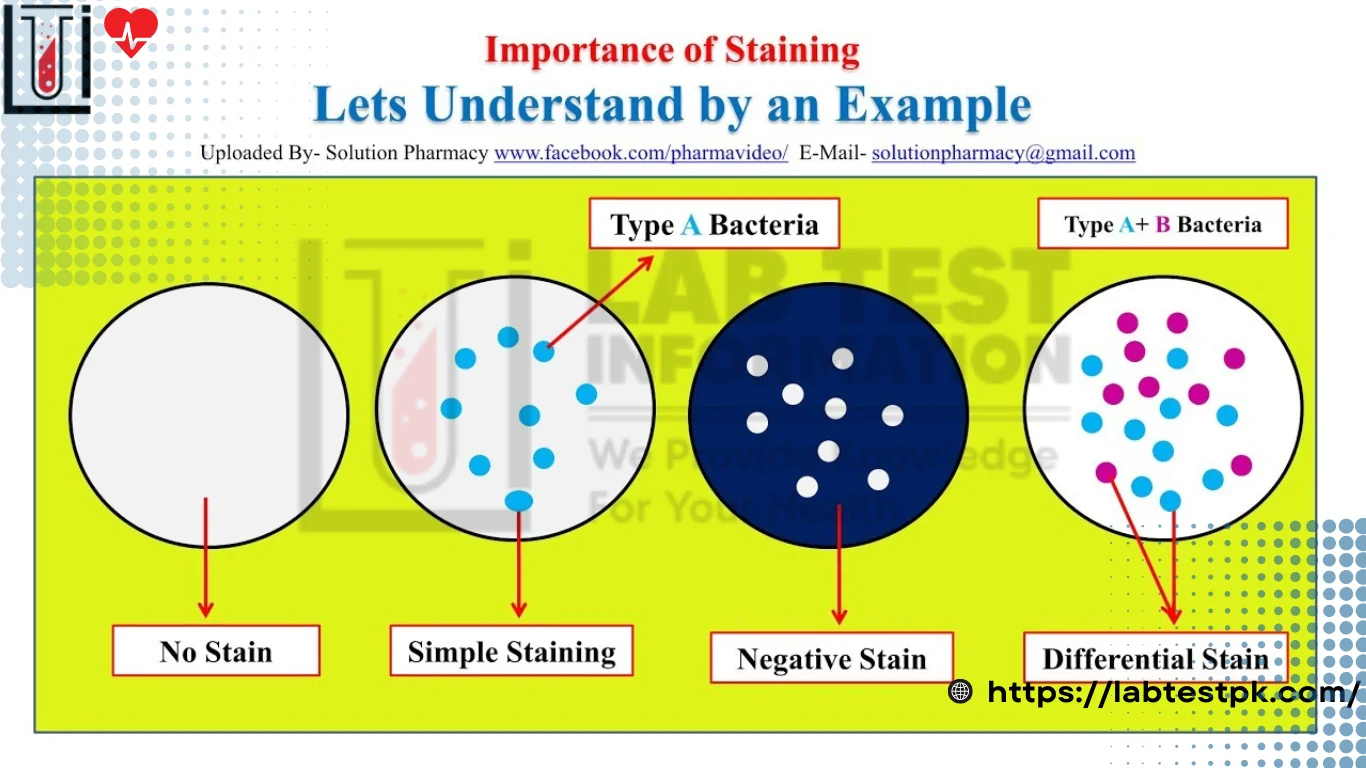
Staining Types, A stain is a substance that adheres to cells giving the cell color. Staining is a Process in which cells of the tissue are colored with a positive stain chemical dye for identification. Most biological Structures are colorless and Transparent so staining is applied to see better contrast.
Types of Staining Techniques:
| Simple staining (use of single stain) | Differential staining (uses of two contrasting Stains Separated by a decolorizing agent) |
| For visualization of (Morphological shape and arrangement) | Identification — Special Stain |
| Gram Stain — Acid-fast Stain for Stain Spores stain for Capsules Stains for flagella stain for the metachromatic granules |
Difference between Simple and Differential Staining of bacteria:
Simple Staining:
Simple staining is a step method using only one dye. Simple staining uses only one reagent and is used to determine the shape, arrangement of microbial, and dimensions.
Differential Staining:
Differential Staining is a Staining Process that uses more than one staining chemical reagents dye to different cellular structures.
Difference:
| Terms of Comparision | Simple Staining | Differential Staining |
| No. of Stain used | Size, shape, and arrangement of bacterial cells | Uses more than one Stain |
| Color imparting | Imparts only one color to bacterial cells | Imparts two or more different colors to bacterial cells |
| Outcome | Imparts two or more different colors to bacterial cells | Size shape and arrangement; Differentiation in groups. Identification of Structures of Bacteria Cells. |
| Examples | •Methylene blue •Crystal violet Staining • Malachite green • Basic fuchsin staining • Safranine staining |
• Gram staining • Acid-fast staining • Endospore staining |
| Procedure | 1- Take a clean grease free slide 2- Prepare Smean on it 3- Air dry and heat fix flood the slide with Stain 4- Allow the stain to react for 2 mint 5- Wash the slide with water 6- Analysis through a microscope to look for objective |
1 Take a clean grease free slide 2-Applying a Primary stain (crystal violet) 3-Adding a mordant (Gram’s iodine) 4-Rapid decolorization with ethanol, acetone, or a mixture of both 5- Counterstaining with Safranin |
| Observation Unstained |
Crystal violet Staining. | G+ve G-ve Gram staining Endospore Endospore staining |

Difference between Invivo and Invitro Staining:
Invitro staining:
In Invitro staining involves coloring cells or structures that have been removed from their biological context.
Invivo Staining:
Invivo means “in life” (as contrasted to in-vitro staining). Invivo staining is the Process of dyeing living tissue.

Difference:
| Terms of Comparision | In-vivo Staining | Invitro Staining |
| Type of Specimen | Living biological | Dead or non-living |
| Types of stain | Spedmen: Vital stains are | Biological specimen Non-vital stains |
| Fixation | Used: No need to fix | Are used fixation is required |
| Outcome | Reveal cytological details of cell or structure: Its form (morphology) or Position within a cell or tissue. Reveal sites where specific chemical reactions are taking place within cells. |
Size Shape and arrangement: Differentiates between groups: Identify structures |
| Examples | Janus Green Staining Trypan blue staining |
Gram staining |
| Observation | Dead cell live cell Trypan blue staining |
G+ve G-ve Gram staining |
Difference between Positive staining and Negative staining:
Positive Staining:
It is also called direct staining. The negatively, charged cell wall of many micro-organisms attracts
The Positively charged chromophore, causes the specimen to absorb the stain giving it the color of the stain being used.
Negative Staining:
It is also called indirect staining. In which bacterial cells are not stained but are made visible against a dark background. Acidic is used in this staining. Acidic staining is a negative charge, therefore it does not fix with the negative charge bacterial cell. On the other hand, it forms deposits around the cell, resulting in the appearance of bacterial cell clusters.

Difference:
| Terms of Comparision | Positive Staining (Direct) | Negative Staining(Indirect) |
| Stain used | Basic Stain | Acidic stain |
| Also known as | Direct stain | Indirect staining |
| Charge of Stain Examples | • Positive charge • Methylene blue Crystal violet • Malachite green |
• Negative charge • Nigrosine • India ink • Eosin, Cong red |
| Heat fixation outcome | Required Stains of the bacterial cells | Not required stains on the background |
| Principle | When a Staining Prundare colors the cells present In a Preparation, but leaves the background collarless (appearing as white) | Negative staining requires the use of an acidic stain. Acidic stain with its negatively changed chromogen. Will not Penetrate the cells because they have a negative charge on the bacterial Surface. |
| Observation | Colorless Colored bacterial cell |
Colored Colorless bacterial cell |
| Procedure | 1- The Procedure of positive Staining first step is to sterilize the inoculation loop over the flame of a bunsen burner and Cool it down for 2-3 mnt. 2- Seundiinent step Dip it in a broth containing bacteria and take a loop full of culture. 3- Third step smear a culture on a glass slide make a thin film and allow the Suspension to completely dry. 4- Quickly pass the slide over a flame 3-4 times to heat fix. 5- let it cool down for a bit Place it over a staining tray and cover this entire thin film with the stain for a few minutes. Dry it and observe the result |
1- Place a small nigrosin close to one end of a clean slide. 2- Using an aseptic technique, place a teofull of inoculum from the bacterial culture in the drop of nigrosin for 4 min. 3- ) Place a slide against the drop of the suspended organism at a 45°C angle and allow the drop to Spread along the slide. 4- Push the Slide away from the drop of suspended to form a thin smear. Air dry. Note: Do not heat fix the Slide. |

You offer some educated points within this entry, but aren’t you generalising something crucial?
[…] IV Method(b) Jeff’s reaction(c) ICT Screening method ✓(d) […]
Have you ever considered creating an e-book or
guest authoring on other websites? I have a blog based upon on the
same subjects you discuss and would really like to have you share some stories/information. I know
my subscribers would appreciate your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to send me an email.
This entry could include so much more 🙁 Could you expand on it in the future?
[…] of a catheter into the cervix. This may lead to the risk of infection, especially if proper aseptic techniques are not […]
[…] Specific gravity […]
[…] bacteria, particularly those belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family. It contains bile salts, crystal violet dye, neutral red dye, and lactose as key […]
[…] the Wire Loop: Ensure the wire loop is clean before each test by dipping it in hydrochloric acid and then rinsing it with distilled […]