Pus Culture and Sensitivity
Pus Culture and Sensitivity, The Pus Culture and Sensitivity test is a laboratory examination performed on a sample of pus collected from an infected area of the body. Pus is a thick, yellowish that contains dead white blood cells, bacteria, and other substances and is typically produced in response to an infection. This pus culture and sensitivity test process involves the following steps:
1- Sample Collection:
- A healthcare professional collects a sample of pus from the infected area using a sterile swab or needle.
- Common sites for collecting pus samples include wounds, abscesses, or infected tissues.
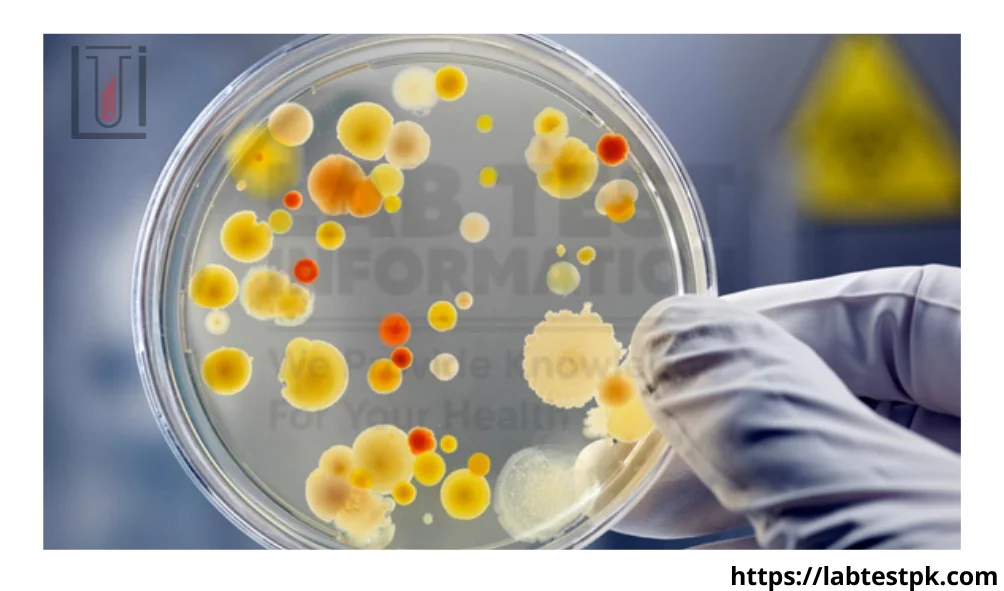
2- Culture:
- The collected pus sample is then cultured in a laboratory.
- Placed on a special medium that encourages the growth of bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms present in the pus.
- The culture is incubated under specific conditions to allow the microorganisms to grow.
3- Identification:
- Once the microorganisms have grown, laboratory technologists analyze the culture to identify the specific types of bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens present in the sample.
- This identification helps determine the exact cause of the infection.
4- Sensitivity fasting:
- After identification, the susceptibility or sensitivity of the isolated microorganisms to various antibiotics or anti-fungal medications is tested.
- This step involves exposing the cultured microorganisms to different antibiotics to see which ones are most effective in inhibiting or killing them.
5- Reporting Result:
- The lab generates a report detailing the identified microorganisms and their susceptibility to various antibiotics.
- The report helps guide healthcare providers in selecting the most appropriate and effective treatment for the specific infection.
- If no germs grow, the culture is negative. while the germs grow, the culture is positive.
Who Should take the Pus Culture Sensitivity Test?
This test is recommended for individuals who have symptoms of an infection, such as
- Fever
- Redness
- Swelling
- Discharge from a wound or other infected area
NOTE
The culture and sensitivity test crucial in guiding healthcare providers in prescribing antibiotics or other medications that can effectively target the specific microorganism causing the infection. The personalized approach helps in treating the infection more effectively, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance, and improving patient outcomes.
FAQs:
- What is Culture and Sensitivity testing?
- Answer: Culture and Sensitivity testing involves growing microorganisms from a clinical sample (such as blood, urine, or sputum) in a laboratory setting and then testing the isolated bacteria or fungi against various antibiotics to determine the most effective treatment.
- Why is Culture and Sensitivity testing important?
- Answer: It helps in identifying the causative agent of an infection and guides healthcare providers in selecting the most appropriate antibiotic treatment. This helps prevent the unnecessary use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and improves the chances of successful treatment.
- What types of clinical samples are commonly used for C&S testing?
- Answer: Common samples include blood, urine, sputum, wound swabs, and cerebrospinal fluid. The choice of sample depends on the suspected site of infection.
- How is a culture done in the laboratory?
- Answer: The clinical sample is inoculated onto a culture medium that provides an environment conducive to the growth of microorganisms. The medium is then incubated, and the resulting colonies are identified and tested.
- What does Sensitivity testing involve?
- Answer: Sensitivity testing (also known as antibiotic susceptibility testing) assesses the response of the isolated microorganism to various antibiotics. It helps determine which antibiotics are most effective against the specific pathogen.
- How is antibiotic susceptibility reported?
- Answer: Results are typically reported as “Sensitive” (the microorganism is susceptible to the antibiotic), “Intermediate” (the microorganism may be susceptible under certain conditions), or “Resistant” (the microorganism is not susceptible to the antibiotic).
- How long does it take to get C&S results?
- Answer: The time frame varies depending on the type of sample and the microorganism. Preliminary results may be available in 24-48 hours, but final results may take several days.
- What if the culture is negative?
- Answer: A negative culture indicates that no significant growth of microorganisms was observed. It suggests that infection may not be present or that the causative agent was not successfully cultured.
- Can C&S be done for viruses?
- Answer: No, Culture and Sensitivity testing is primarily used for bacteria and fungi. Viruses require different methods for detection, such as molecular or serological tests.
- Are there limitations to C&S testing?
- Answer: Yes, some microorganisms may be challenging to culture, and the results may be influenced by the quality of the sample collected. Additionally, the test provides information on susceptibility at a specific point in time, and resistance patterns can change over time.

[…] may necessitate further evaluation based on clinical judgment. The accuracy of the test can be influenced by factors such as the timing of sample collection, the stage of the illness, and the overall […]
[…] and growth of Microorganisms or germs in the body. Microorganisms that cause infections are Viruses, Bacteria, Fungi, and parasites. An infection occurs when germs enter the body increase in number and cause a […]
[…] can provide significant insights into our well-being. In this article, we’ll delve into what pus cells are, why they might appear in urine, and what steps can be taken for a healthier urinary […]