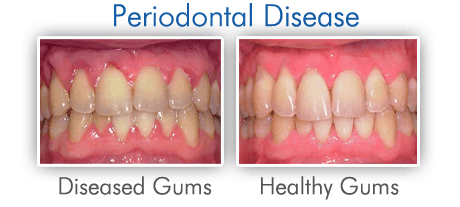
Periodontal Disease, A periodontal disease is a diverse group of inflammatory diseases that affect the Periodontium and is the most common chronic infection in adults. The Periodontium is the supporting structure of a tooth and includes the cementum, the periodontal membrane of a tooth, the bones of the jaw, and the gingivae (gums).
It is mainly the result of infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth- In gingivitis, the gums can become swollen and red and bleed.
There are two main stages of periodontal disease:
-
Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. It occurs when plaque accumulates on the gumline, causing inflammation. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene and professional dental cleaning.
-
Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. At this stage, the inflammation spreads deeper, affecting the bone and connective tissues that support the teeth. Gums may start to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that harbor more bacteria. Over time, the bones, gums, and tissue supporting the teeth are destroyed, potentially leading to tooth loss.
Symptoms Periodontal Disease:
- Gums that are receding or pulling away from teeth
- Red Swallow or tender Jums
- Bleeding, flossing, or eating hard foods
- Bad taste in your mouth
- Bone Destruction
Diagnosis:
- The dentist will examine your gums.
- Examine your teeth.
Treatment:
Antibiotics include:
- Tetracycline hydrochloride
- Minocycline
- Doxycycline
It can be controlled by frequent Plaque removal by brushing, flossing, and rinsing with mouthwashes, and at times by gums surgery and antibiotics.


[…] Metabolic Alkalosis VomitingAlkali therapyUrinary tract infection […]
[…] some cases, if you are allergic to penicillin, alternative antibiotics may be prescribed, such as doxycycline or […]
[…] Metabolic AlkalosisVomitingAlkali therapyUrinary tract infection […]
[…] harsh or abrasive mouthwashes that may irritate your […]
[…] of about 2-3 months), the fructosamine test reflects changes in blood sugar levels over a shorter period, typically 2-3 […]