Oxygen Saturation Test Spo2
Oxygen Saturation Test Spo2 A test measures the amount of oxygen red blood cells carry. One method uses a device that shines light through a finger. The device measures the amount of oxygen in the blood based on how red blood cells carrying oxygen absorb and reflect light. It is also called Arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) if measured in arterial blood and Venous oxygen Saturation (SaO2) if measured in venous blood.
With the help of this parameter of arterial blood, gases test, we can measure the percentage of oxygen-bound hemoglobin (oxyhemoglobin) in the blood For proper functioning of the body we need a certain level of oxygen in our blood. Our body maintains healthy SPO2 levels through breathing. Oxygen saturation may be measured with arterial blood gases through pulse oximetry.
Causes of High Oxygen Saturation:
- High Dose of Oxygen therapy
- Lung disease
Causes of Low Oxygen Saturation:
- Sleep Apnea
- Smoking
- Anemia
- Pneumonia
- Emphysema
- Asthma
- Hepatitis B”>Viral Infection
- Pneumothorax
- Bronchitis
- Intestinal Lung Disease
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Congenital Heart Disease
- Low Level of Atmospheric oxygen
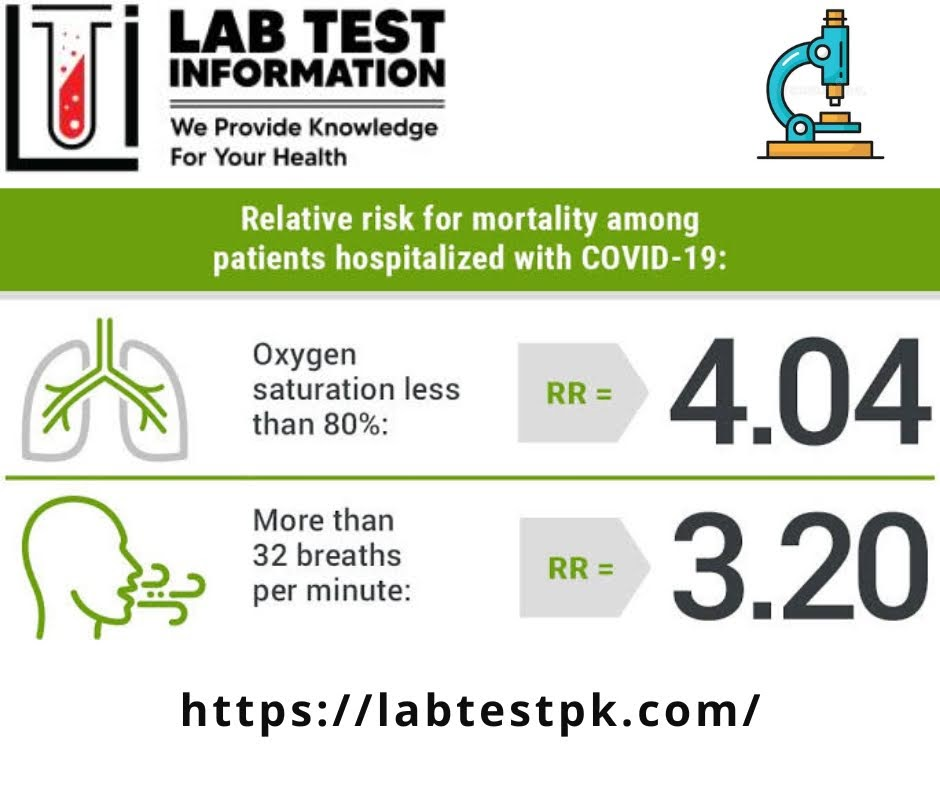
Normal Range of Oxygen Saturation (Spo₂):
(SpO2) oxygen Saturation (Arterial Blood): 95% to 100%
(SpO₂) oxygen saturation (Venous Blood): 70%. to 75%
Tests used include:
Pulse Oximetry Blood gas test
Long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT) assessment
Hypnic challenge (fitness-to- fly test)

How to Performed Test:
Procedure:
- Take a sample of your blood from your arm with a needle.
- If you take any medications or supplements, they can affect the results. So can eating grapes and fruits that are high in acid.
- Collect at least 2 mL of arterial blood or venous blood in heparinized Syringes, if the test is in a Green top tube with sodium heparin or lithium Heparin Mix the Sample immediately The test only fluid in your blood, not the blood cells or the platelets that help your blood clot. Now, Add the aid to the liquid to unlock Carbon dioxide from the bicarbonate. The amount of bicarbonate is measured by how fat the sample’s acidity changes.
NOTE:
Oxygen saturation is also measured through pulse oximetry.
Result:
The oximeter display shows the percentage of oxygen your in blood. For someone healthy, the normal blood oxygen saturation level will be around 95-100% if the oxygen level is below then it can indicate there is a long-term problem.

[…] Toxic H₂O2 can cause intracellular damage such as damage to DNA, Lipid, and proteins. To remove H2O2 and other similar compounds, cells Produce catalase enzyme to break down H2O2 into liquid water (H2O) and oxygen (Or) 2H2O2 Catalase 2H2O + O₂. […]
[…] CNS occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. Like other organs, the brain also needs oxygen and nutrients provided by blood to function properly. If the supply of blood to the brain is […]
[…] main function of erythropoietin is to respond to low oxygen levels in the body, a condition known as hypoxia. When the oxygen levels in the blood are […]
[…] are released by the bone marrow in response to low RBC levels to help compensate for the decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of the […]
[…] methemoglobin. Methemoglobin cannot bind oxygen effectively, and as a result, it reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of […]
[…] Pulmonary Fibrosis […]
[…] oxygen to the Cells in muscles (myocytes). All cells in your body need oxygen to function. They use oxygen to convert stored. Energy It provides oxygen to working […]
[…] blood cells, which carry oxygenWhite blood cells, which fight infectionHemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood […]
[…] O2 Saturation (Oxygen Saturation) […]