Insulin Fasting Blood Test
Insulin Fasting Blood Test, An insulin fasting blood test, also known as a fasting insulin test, is a medical test used to measure the concentration of insulin in your blood after a period of fasting. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar (glucose) levels in your body. It helps to transport glucose from your bloodstream into your cells, where it can be used for energy or stored for future use.
Here’s how a fasting insulin blood test typically works:
The fasting insulin test is often used in conjunction with other tests, such as fasting blood glucose levels and an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), to get a more comprehensive view of your glucose metabolism. These tests can help diagnose conditions like prediabetes, diabetes, and insulin resistance.
Types of Insulin Fasting Blood Test:
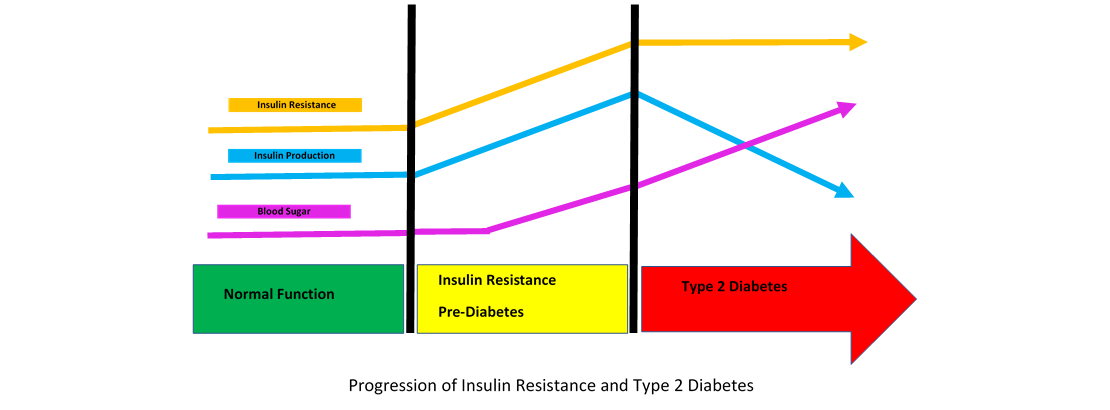
A fasting blood test for insulin measures the level of insulin in your blood after an overnight fast. This test is used to assess insulin resistance, diabetes, and other conditions related to insulin regulation in the body. There are different types of insulin fasting blood tests:
- Fasting Insulin Test (Fasting Insulin Level): This is the most common type of insulin fasting blood test. It measures the concentration of insulin in your blood after an overnight fast. Typically, you’ll fast for 8-12 hours before the test. Elevated fasting insulin levels may indicate insulin resistance or other underlying metabolic conditions.
- C-Peptide Test: C-peptide is a protein that is produced at the same time as insulin. A C-peptide test measures the level of C-peptide in your blood after fasting. This test can help determine if your body is producing an appropriate amount of insulin. High C-peptide levels might suggest that your pancreas is producing too much insulin, which could be due to insulin resistance or other factors.
- HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance): This is not a direct insulin measurement but a calculated index used to assess insulin resistance based on fasting glucose and insulin levels. It’s often used in research and clinical settings to estimate insulin sensitivity. A higher HOMA-IR score indicates greater insulin resistance.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): While this is not a fasting test, it’s worth mentioning because it involves measuring insulin levels. You’ll initially fast overnight, and then, after fasting blood samples are taken, you’ll drink a glucose solution. Blood samples are taken at various intervals afterward to measure glucose and insulin levels. This test helps diagnose diabetes and assess how your body handles glucose and insulin.
- Fasting Blood Sugar (Fasting Glucose) Test: Although this doesn’t directly measure insulin levels, it’s often performed alongside insulin tests. Fasting blood sugar measures the amount of glucose in your blood after an overnight fast. Elevated fasting glucose levels can be indicative of diabetes or impaired glucose metabolism, which often goes hand-in-hand with insulin issues.
Symptoms of Low and High Insulin Fasting Levels:
Here are the symptoms and implications of low and high insulin levels as indicated by a fasting blood test:
Symptoms of Low Insulin (Hyperglycemia):
- High Blood Sugar Levels: The primary indicator of low insulin is elevated blood sugar levels, which can be detected through a fasting blood glucose test. A fasting blood glucose level above 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) is typically considered diabetic, while levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL are considered prediabetic.
- Increased Thirst: Excessive thirst (polydipsia) is a common symptom of high blood sugar levels, as your body tries to flush out excess glucose through increased urine production.
- Frequent Urination: High blood sugar levels can lead to frequent urination (polyuria) as your kidneys work to remove excess glucose from the blood.
- Fatigue: Low insulin levels can prevent glucose from entering your cells to be used as energy, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite an increase in appetite, individuals with low insulin levels may experience unexplained weight loss because the body is unable to properly use glucose for energy.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can cause changes in the shape of the lens in your eye, leading to blurry vision.
- Frequent Infections: High blood sugar can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, especially yeast infections.
Symptoms of High Insulin (Hypoglycemia):
- Low Blood Sugar Levels: Elevated insulin levels can cause your blood sugar levels to drop too low, leading to hypoglycemia. A fasting blood glucose level below 70 mg/dL is typically considered hypoglycemic.
- Shakiness and Tremors: One of the early signs of hypoglycemia is feeling shaky, jittery, or having tremors.
- Sweating: Profuse sweating, even when you’re not hot, can be a sign of low blood sugar.
- Anxiety and Nervousness: Hypoglycemia can cause feelings of anxiety, nervousness, or irritability.
- Rapid Heartbeat: Your heart rate may increase (tachycardia) when you have low blood sugar.
- Hunger: A strong desire to eat, even if you’ve recently had a meal, can be a symptom of high insulin levels leading to low blood sugar.
- Confusion and Difficulty Concentrating: Hypoglycemia can affect cognitive function, leading to confusion and difficulty concentrating.
- Weakness and Fatigue: As your body struggles to provide energy to your cells, you may feel weak and fatigued.
Why I need an Insulin Fasting Blood Test:
This test provides important information about your insulin production and how your body is processing glucose (sugar). Here are several reasons why you might need this test:
- Diabetes Diagnosis: Fasting insulin tests are often used to help diagnose diabetes and other glucose metabolism disorders. Elevated fasting insulin levels can be indicative of insulin resistance, a common precursor to type 2 diabetes.
- Monitoring Diabetes Treatment: For individuals with diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, tracking fasting insulin levels can help assess the effectiveness of treatment, including lifestyle changes and medications. It can show if insulin resistance is improving or worsening.
- Gestational Diabetes: Pregnant women may undergo fasting insulin tests as part of screening for gestational diabetes, a temporary form of diabetes that can develop during pregnancy.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS often have insulin resistance, which can lead to elevated fasting insulin levels. This test may be used to aid in the diagnosis of PCOS.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Fasting insulin tests are sometimes used as part of the evaluation for metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance is one of the key components of metabolic syndrome.
- Hypoglycemia: In some cases, this test may be used to investigate the cause of recurrent low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). High fasting insulin levels can sometimes be associated with certain rare conditions that cause hypoglycemia.
- Research and Personalized Medicine: Fasting insulin tests are also used in clinical research to better understand insulin resistance and related metabolic conditions. They can help tailor treatment plans for individuals with specific insulin-related issues.
- Overall Health Assessment: Your healthcare provider may order a fasting insulin test as part of a comprehensive health assessment to evaluate your risk of developing diabetes or cardiovascular diseases.
What does the Insulin Fasting Blood Test Result mean:
Here’s what different results of the Insulin Fasting Blood Test can mean:
- Normal Insulin Levels: A normal fasting insulin level typically falls between 2 to 25 micro international units per milliliter (IU/mL), although the specific reference range can vary slightly depending on the laboratory. If your result falls within this range, it generally indicates that your body is effectively regulating blood sugar levels.
- Low Insulin Levels: If your fasting insulin levels are lower than the normal range, it could suggest that your pancreas is not producing enough insulin. This can be seen in conditions like Type 1 diabetes, where the pancreas doesn’t produce any insulin, or in some rare medical conditions.
- High Insulin Levels: Elevated fasting insulin levels can indicate insulin resistance, which is often associated with conditions such as Type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). In these conditions, your body produces insulin, but your cells do not respond to it effectively, leading to higher insulin levels in an attempt to control blood sugar.
- Impaired Fasting Glucose: Sometimes, high fasting insulin levels can be accompanied by high fasting blood glucose levels, which may suggest early stages of insulin resistance or prediabetes. This means your body is struggling to keep your blood sugar within the normal range, but you haven’t yet reached the criteria for a diabetes diagnosis.
- Other Factors: It’s important to note that fasting insulin levels can be influenced by various factors, including diet, physical activity, medications, and other medical conditions. Interpretation of the results should be done in the context of your overall health and medical history.
Treatment of Insulin Fasting Levels:
Here’s how the treatment or interpretation of the results may vary depending on the outcomes:
- Normal Results:
- If your fasting insulin levels fall within the normal range, it suggests that your body is effectively regulating blood sugar levels. No specific treatment is required for insulin levels in this case.
- High Insulin Levels with Normal Blood Sugar:
- High fasting insulin levels, especially when blood sugar levels are normal, could indicate insulin resistance. Treatment may involve lifestyle changes:
- Dietary Modification: A balanced diet with a focus on complex carbohydrates, fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help improve insulin sensitivity.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can enhance insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Weight Management: If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
- In some cases, medication or insulin therapy may be necessary if lifestyle changes are insufficient.
- High fasting insulin levels, especially when blood sugar levels are normal, could indicate insulin resistance. Treatment may involve lifestyle changes:
- High Insulin Levels with High Blood Sugar:
- Elevated fasting insulin levels along with high blood sugar are often indicative of type 2 diabetes or other metabolic disorders. Treatment may include:
- Medications: Oral medications, insulin therapy, or other injectable medications may be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Dietary changes, exercise, and weight management are still essential components of managing type 2 diabetes.
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent monitoring of blood sugar levels and periodic follow-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial to managing and adjusting treatment as needed.
- Elevated fasting insulin levels along with high blood sugar are often indicative of type 2 diabetes or other metabolic disorders. Treatment may include:
- Low Insulin Levels:
- Low fasting insulin levels could suggest certain medical conditions, such as type 1 diabetes, late-stage type 2 diabetes, or other rare disorders affecting insulin production. Treatment typically involves:
- Insulin Therapy: If you have type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes, you will likely need insulin replacement therapy.
- Medical Evaluation: Further tests and examinations are needed to determine the underlying cause of low insulin levels.
- Low fasting insulin levels could suggest certain medical conditions, such as type 1 diabetes, late-stage type 2 diabetes, or other rare disorders affecting insulin production. Treatment typically involves:




[…] function, particularly the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is a measure of how well the kidneys are filtering waste products from the […]
[…] is involved in the regulation of glucose metabolism and fatty acid breakdown. It enhances insulin sensitivity, which means it helps the body respond more effectively to insulin, a hormone that […]
[…] inhibit a rise in blood glucose levels in diabetic patients to […]
[…] long-term or historical use. Detection times can vary depending on the drug, the individual’s metabolism, and the sensitivity of the test. In some cases, false positives or negatives can occur, so […]
[…] of your blood glucose levels when you haven’t eaten for an extended period. Normal fasting blood glucose levels are typically between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter […]
[…] Tremors […]
[…] Fatigue. […]
[…] involves blood tests to measure GH levels. Doctors may also use provocative tests, like the insulin tolerance test or the growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) stimulation test, to confirm the […]
[…] most common method for G6PD screening is a simple blood test, usually done via venipuncture (drawing blood from a vein). Blood is typically drawn from a vein in […]