G6PD Screen Test
G6PD Screen Test, A G6PD screen test is a medical test used to determine the levels of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) enzyme in the blood. G6PD is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in protecting red blood cells from damage caused by certain substances, including certain foods, drugs, and infections.
Purpose of G6PD Screen Test:
The main purpose of this test is to identify whether an individual has G6PD deficiency, a genetic condition that affects the red blood cells. Here’s why the G6PD screen test is important:
- Diagnosis of G6PD Deficiency: The primary purpose of the G6PD screen test is to diagnose G6PD deficiency. This is an inherited condition that primarily affects males, although females can be carriers. People with G6PD deficiency have lower levels or impaired activity of the G6PD enzyme, which can lead to hemolytic anemia, a condition where red blood cells break down more easily than normal.
- Identifying Susceptibility to Hemolysis: G6PD deficiency makes red blood cells more vulnerable to oxidative stress. Certain foods, medications, infections, and other factors can trigger hemolysis (the destruction of red blood cells) in individuals with this deficiency. Identifying G6PD deficiency through screening can help doctors and patients avoid substances and conditions that can trigger hemolysis.
- Preventing Hemolytic Anemia: By identifying G6PD deficiency, healthcare providers can help patients and their families take preventive measures to avoid situations that might lead to hemolytic anemia. This might involve avoiding specific medications, foods, or environmental factors that can cause oxidative stress.
- Guiding Medication Choices: Some medications can induce hemolysis in individuals with G6PD deficiency. Knowing a patient’s G6PD status can help healthcare providers choose alternative medications that are less likely to cause harm.
- Preoperative Screening: G6PD screening may be done before certain surgical procedures that might require blood transfusions. This helps ensure that the blood used for transfusion is compatible with the patient’s G6PD status to prevent complications.
- Genetic Counseling: Identifying G6PD deficiency through screening can also be valuable for genetic counseling. This allows individuals and families to understand the genetic inheritance pattern of the condition and make informed decisions about family planning.
In summary, the G6PD screen test is important for diagnosing and managing G6PD deficiency, which can lead to hemolytic anemia and other health complications. It allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions about medication and treatment choices and helps individuals and families take precautions to avoid triggers for hemolysis.
When G6PD Screen Test ordered?
A G6PD (Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase) screen test is typically ordered by a healthcare provider when there is a suspicion of G6PD deficiency. G6PD deficiency is a genetic condition that affects red blood cells and can lead to a condition called hemolytic anemia, which is characterized by the premature destruction of red blood cells.
Common reasons for ordering a G6PD screen test include:
- Family History: If there is a family history of G6PD deficiency, a healthcare provider may order a screening test for individuals at risk, such as newborns or family members of known G6PD-deficient individuals.
- Jaundice: If a person, especially an infant, presents with jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), a G6PD screen may be ordered to determine if G6PD deficiency is the underlying cause.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as certain antibiotics and antimalarial drugs, can trigger hemolysis (the breakdown of red blood cells) in individuals with G6PD deficiency. If a person is prescribed one of these medications, a G6PD screen may be ordered as a precaution.
- Prior Hemolytic Episodes: Individuals who have experienced unexplained episodes of hemolysis may be screened for G6PD deficiency to determine if it is the underlying cause.
- Before Certain Medical Procedures: In some cases, a G6PD screen may be ordered before certain medical procedures or surgeries to assess the risk of hemolysis during the procedure.
- As part of Newborn Screening: G6PD screening is included as part of newborn screening programs in some regions to identify infants with the condition early on.
Test Procedure of G6PD Screen?
Here’s a general outline of the procedure for a G6PD screening test:
1. Patient Preparation:
- Explain the test to the patient and obtain informed consent if necessary.
- Inform the patient if there are any dietary or medication restrictions before the test.
2. Blood Sample Collection:
- The most common method for G6PD screening is a simple blood test, usually done via venipuncture (drawing blood from a vein). Blood is typically drawn from a vein in the arm.
3. Laboratory Analysis:
- The collected blood sample is sent to a clinical laboratory for analysis.
- In the laboratory, the blood sample is processed to separate the serum (the liquid portion of blood) from the cellular components.
4. G6PD Enzyme Activity Assay:
- The laboratory technician will perform an assay to measure the activity of the G6PD enzyme in the serum.
- The most commonly used assay for G6PD activity is the quantitative spectrophotometric assay, which measures the rate of change in the absorbance of light at a specific wavelength as the enzyme reacts with a substrate.
- The results are reported in units per gram of hemoglobin or as a percentage of normal G6PD activity.
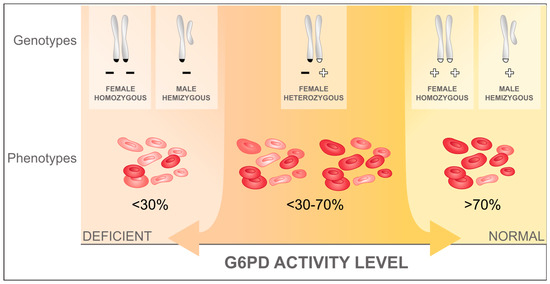
5. Interpretation of Results:
- The results are interpreted to determine if the individual has normal G6PD enzyme activity, is a carrier (heterozygous), or has G6PD deficiency (hemizygous or homozygous).
- Normal G6PD activity indicates that the person is not deficient.
- Reduced G6PD activity indicates the presence of G6PD deficiency.
6. Reporting and Consultation:
- The results are reported to the healthcare provider who ordered the test.
- The healthcare provider will discuss the results with the patient and provide appropriate guidance or treatment recommendations if necessary.
Interpretation of results G6PD Screen:
Here are some possible interpretations of G6PD screen results:
- Normal G6PD Activity:
- If the G6PD screen shows normal enzyme activity, it means that the individual has sufficient levels of functional G6PD, and they are not deficient in this enzyme.
- This is the expected result for most individuals, and it suggests that their red blood cells are adequately protected from oxidative stress.
- G6PD Deficiency:
- If the G6PD screen reveals reduced enzyme activity, it may indicate G6PD deficiency. G6PD deficiency is a genetic condition where the enzyme is not produced in sufficient quantities or is less functional.
- The severity of the deficiency can vary, and it can be classified into different variants, such as mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of enzyme activity.
- The specific classification of deficiency will depend on the laboratory’s reference ranges and the values obtained from the test.
- Further Testing Required:
- Sometimes, G6PD screening may yield inconclusive results or results that fall in a gray area.
- In such cases, further confirmatory tests, like G6PD enzyme quantification or molecular genetic testing, may be necessary to determine the exact status of G6PD deficiency and its severity.
- Interpretation Variability:
- The interpretation of G6PD screen results can vary depending on the laboratory, the assay method used, and the reference ranges established by that particular lab.
- It’s essential to consider the specific laboratory’s reference ranges when interpreting results.
- Clinical Implications:
- G6PD deficiency can lead to hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) when exposed to certain triggers, such as certain foods, drugs, or infections.
- The interpretation of G6PD screen results should also consider the clinical history of the patient and any signs or symptoms of hemolysis.
Treatment of G6PD Screen:
The treatment of G6PD (Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase) deficiency primarily involves managing the condition to prevent hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) triggered by certain factors. G6PD deficiency is a genetic condition, so there is no cure, but the goal is to minimize the risk of hemolysis and its associated complications. Treatment and management strategies typically include:
- Avoiding Triggers: The most important aspect of managing G6PD deficiency is avoiding substances and situations that can trigger hemolysis. These triggers can include certain foods, drugs, and infections. Some common triggers include fava beans, certain antibiotics (e.g., sulfa drugs), antimalarial medications (e.g., primaquine), and infections like hepatitis. Individuals with G6PD deficiency should be educated about these triggers and instructed to avoid them.
- Medication Management: If a person with G6PD deficiency requires medication, healthcare providers should be aware of the condition to prescribe alternatives that are less likely to cause hemolysis. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional before taking any medications or supplements.
- Folic Acid Supplementation: Some individuals with G6PD deficiency may benefit from folic acid supplementation because they can have a higher risk of developing anemia. Folic acid can help support the production of red blood cells.
- Manage Infections Promptly: Infections can trigger hemolysis in individuals with G6PD deficiency. It’s crucial to promptly treat any infections and follow your healthcare provider’s advice.
- Blood Transfusions: In severe cases of hemolysis or anemia, blood transfusions may be necessary to replace the damaged red blood cells with healthy ones.
- Education and Awareness: Patients and their caregivers should be educated about the condition and its triggers. They should also have access to medical alert bracelets or cards indicating their G6PD deficiency so that healthcare providers can make informed decisions about their treatment.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a well-balanced diet and regular exercise, can help support overall health and reduce the risk of complications.
It’s important to note that the severity of G6PD deficiency can vary among individuals, and not all individuals will experience symptoms or complications. Management and treatment plans should be individualized based on the specific needs and circumstances of each person. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a genetic counselor is essential for proper management and guidance regarding G6PD deficiency. Additionally, as medical knowledge and guidelines may change over time, it’s important to seek the most up-to-date information from healthcare professionals.



Start Your Search for Real Estate in Bali Now
[…] Omega 3 & 6 Fatty Acids are essential polyunsaturated fats that play crucial roles in maintaining overall health. They are termed “essential” because the human body cannot produce them on its own, so they must be obtained through diet or supplements. […]
[…] of hemolytic anemia includes avoiding suspect medications, treating related infections, and taking drugs that suppress […]
[…] the differentiation and identification of bacterial species based on their growth characteristics, hemolytic patterns, and metabolic […]