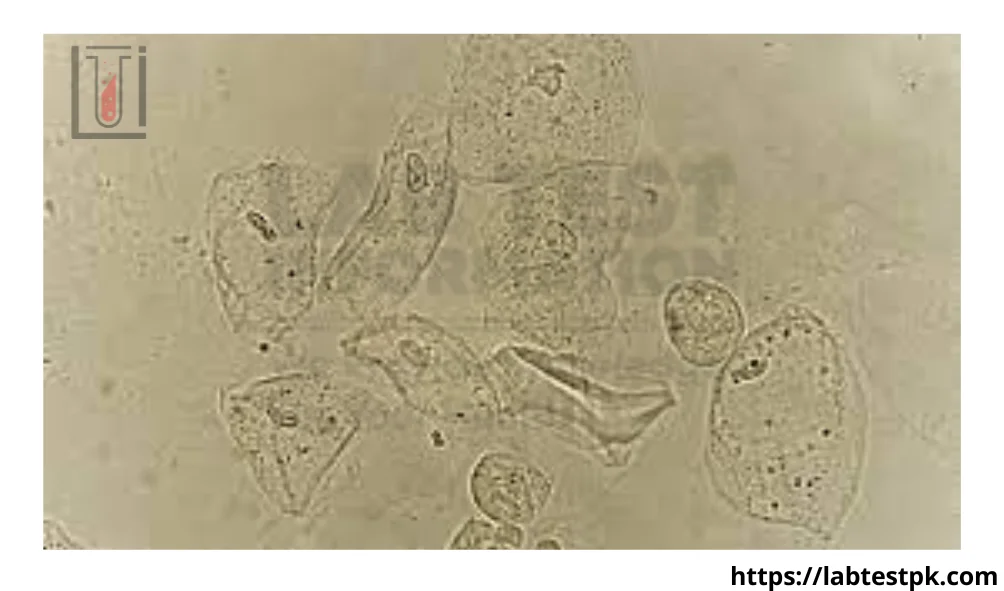
Epithelial Cells In Urine, Epithelial cells are cells that make up the lining of various organs and structures in the body, including the urinary tract. When we talk about epithelial cells in urine, we are referring to the presence of these cells in a urine sample.
The urinary tract consists of structures like the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, and each of these structures is lined with epithelial cells. Normally, a small number of epithelial cells may be present in urine, and this is considered normal. However, an elevated or abnormal level of epithelial cells in urin could indicate an underlying issue.
The presence of epithelial cells in urine may be associated with conditions such as urinary tract infections, kidney disorders, or inflammation in the urinary tract. The type and quantity of epithelial cells present can provide information about the location and nature of the potential problem.
Outline:
-
Introduction
- A brief definition of epithelial cells in urine
- Importance of monitoring urinary epithelial cells
-
Types of Epithelial Cells
- Squamous epithelial cells
- Transitional epithelial cells
- Renal tubular epithelial cells
- #
- Describing the normal presence of epithelial cells
- Indicators of abnormal levels
-
Causes of Elevated Epithelial Cells
- Infections
- Inflammatory conditions
- Renal disorders
-
Diagnostic Procedures
- Urinalysis
- Microscopic examination
- Advanced imaging techniques
-
Interpreting Results
- Understanding the significance of epithelial cell counts
- Correlation with other urinary components
-
Health Implications
- The link between epithelial cells and urinary tract health
- Potential implications for overall health
-
Treatment Approaches
- Addressing underlying causes
- Lifestyle modifications
-
Preventive Measures
- Hydration
- Regular health check-ups
- Dietary considerations
-
Impact on Specific Demographics
- Epithelial cells in pediatric urine
- Considerations for the elderly
-
Myths and Misconceptions
- Common misunderstandings about epithelial cells in urine
- Dispelling myths with scientific facts
-
Latest Research and Discoveries
- Ongoing studies on urinary epithelial cells
- Potential breakthroughs in detection and treatment
-
Patient Awareness
- Educating individuals about the importance of urinary health
- Encouraging regular screenings
-
Conclusion
- Summarizing key points
- Emphasizing the significance of monitoring epithelial cells in urine
Types of Epithelial Cells
Epithelial cells in urine can be classified into three main types: squamous, transitional, and renal tubular epithelial cells. Each type provides unique insights into the health of different parts of the urinary system.
Squamous epithelial cells are typically derived from the urethra and vagina, representing the lower urinary tract. Transitional epithelial cells are found in the bladder and upper urinary tract, while renal tubular epithelial cells originate from the kidneys.
Normal vs. Abnormal Presence
Under normal circumstances, a small number of epithelial cells may be present in urine. However, elevated levels could indicate an underlying issue. Understanding the normal presence and recognizing indicators of abnormal levels is crucial for accurate health assessments.
Causes of Elevated Epithelial Cells
Several factors can lead to increased epithelial cells in urine, including infections, inflammatory conditions, and renal disorders. Identifying the root cause is essential for developing effective treatment strategies.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing the presence of epithelial cells involves comprehensive urinalysis, microscopic examination, and, in some cases, advanced imaging techniques. These procedures help healthcare professionals gain a detailed understanding of the urinary system’s condition.
Interpreting Results
Interpreting the results of epithelial cell counts requires a nuanced understanding of their significance. Correlation with other urinary components aids in forming a comprehensive health assessment.
Health Implications
Epithelial cells in urine are not just indicators of urinary tract health; they can also provide insights into broader health implications. Understanding these connections is vital for proactive healthcare.
Treatment Approaches
Addressing elevated epithelial cell levels involves treating the underlying causes, whether they be infections, inflammation, or renal disorders. Lifestyle modifications may also play a crucial role in managing urinary health.
Preventive Measures
Preventing elevated epithelial cell levels involves adopting simple yet effective measures such as hydration, regular health check-ups, and dietary considerations.
Impact on Specific Demographics
The presence of epithelial cells in urine may vary among different demographics, including children and the elderly. Understanding these variations allows for more targeted healthcare interventions.
Myths and Misconceptions
Dispelling common myths and misconceptions about epithelial cells in urine is essential for promoting accurate health information. Addressing misunderstandings with scientific facts ensures informed decision-making.
Latest Research and Discoveries
Ongoing studies on urinary epithelial cells are contributing to the continuous evolution of diagnostic methods and treatment approaches. Staying informed about the latest research is crucial for healthcare advancements.
Patient Awareness
Educating individuals about the importance of urinary health and encouraging regular screenings empowers people to take charge of their well-being. Increased awareness leads to proactive healthcare practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the indicators of urinary health, particularly the presence of epithelial cells is pivotal for proactive healthcare. By staying informed, addressing underlying causes, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can contribute to their overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can the presence of epithelial cells in urine be entirely normal?
- Yes, a small number of epithelial cells in urine is considered normal. However, elevated levels may indicate an underlying issue.
- What are the common symptoms associated with elevated epithelial cell levels?
- Symptoms may include pain or discomfort during urination, frequent urination, and changes in urine color or odor.
- How often should individuals undergo urinalysis to monitor epithelial cell levels?
- The frequency of urinalysis depends on individual health conditions and risk factors. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable.
- Are there specific dietary recommendations for maintaining urinary health?
- Staying hydrated and consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables contributes to urinary health.
- Can stress or lifestyle factors influence epithelial cell levels in urine?
- Stress and certain lifestyle factors may indirectly impact urinary health. Managing stress and adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being.

[…] People with diabetes are at an increased risk of kidney problems. Elevated levels of albumin in the urine can be an early sign of diabetic nephropathy, a kidney condition associated with […]
[…] supports lipid balance. Choosing healthier fats and limiting processed foods further enhances dietary contributions to lipid […]
[…] Carefully: Your healthcare provider will provide instructions on how to collect and store the urine sample […]
[…] a very ugly disease. Fanconi syndrome is a defect in the proximal convoluted tubule; it is known as Renal Tubular acidosis type 2, also known as Proximal Renal Tubular Acidosis and Fanconi […]