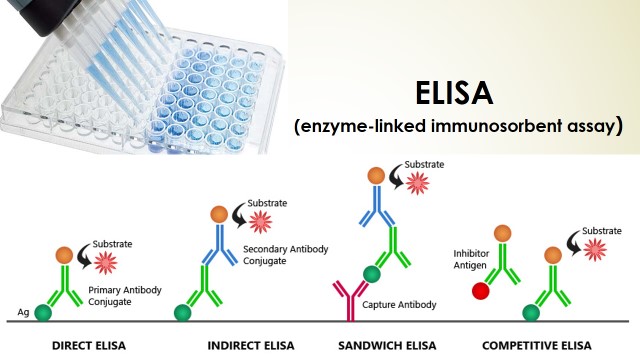
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test procedure was prepared to detect antibodies or antigens in the blood sample. A lot of tests are done by this method. The following are some of the tests performed using the Elisa method.
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
- HBV ( Hepatitis B Virus
- HCV ( Hepatitis C Virus)
- Typhoid
- MP (Malaria) etc.
This test is done in two ways
- Double antibody method/ Antigen detection
- Indirect method/ Antibody detection
Double Antibody Method / Antigen Detection Principle
Requirement:
Wells – Ab coated, Patient sample, Wash solution, Enzymes conjugate, Substrate, Stop solution, Automatic pipet, (10 to 100 ul – 1000 ul), Analyzer, (Semi-automatic chemistry analyzer), or plate reader or strip reader.
Procedure:
Take the antibody-coated well, Now put the sample of the patient in it and incubate for a specific time. Meanwhile, the antigen present in the sample forms a complex by combining with the antibodies Ab- Attached to the gene wells. Then wash the wells thoroughly three to four times with the wash solution to wash away all the excess antigens and antibodies. Now the conjugate or enzyme antibody is added to the wells. Which react with pre-existing complexes to form an Ab-Ag-Ab* complex. Incubate for a specific time and wash the wash with solution three to four times. Now to check the performance of these enzymes, a specific type of substrate is added to it. It changes the color due to the presence of enzymes in the substrate wells. The lack or excess of color is determined with the help of the specific type of analyzer.

Indirect method/ Antibody detection
Procedure:
Take antigen-coated well, Now put the sample of the patient in it and incubate for a specific time. Meanwhile, the antibody present in the sample forms a complex by combining with the antigen Ag- Attached to the gene wells. Then wash the wells thoroughly three to four times with the wash solution to wash away all the excess antigens and antibodies.
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Now the conjugate or enzymes (Anti Immunoglobulin) is added to the wells. Which react with pre-exciting complexes to form an Ag-Ab-Ig* complex. Incubate for a specific time and wash the wash with solution three to four times. Now to check the performance of these enzymes, a specific type of substrate is added to it.
It changes the color due to the presence of enzymes in the substrate wells. The lack or excess of color is determined with the help of the specific type of analyzer. If the color intensity of the Substrate is greater than the normal color, the sample contains an antibody.

[…] Hepatitis B is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) and can lead to both acute and chronic forms of the disease. […]
[…] Vitamin B1 helps to boost our immune System. […]
[…] factors: Inherited enzyme deficiencies can result in a higher predisposition to methemoglobinemia. For example, deficiencies […]