Complement C3 Test is a protein that plays a critical role in the complement system, which is a part of the immune system responsible for enhancing the body’s ability to fight off infections and clear out damaged cells. The complement system consists of a group of proteins that work together to help antibodies and phagocytic cells (cells that can ingest and digest foreign particles) identify and destroy pathogens like bacteria and viruses.
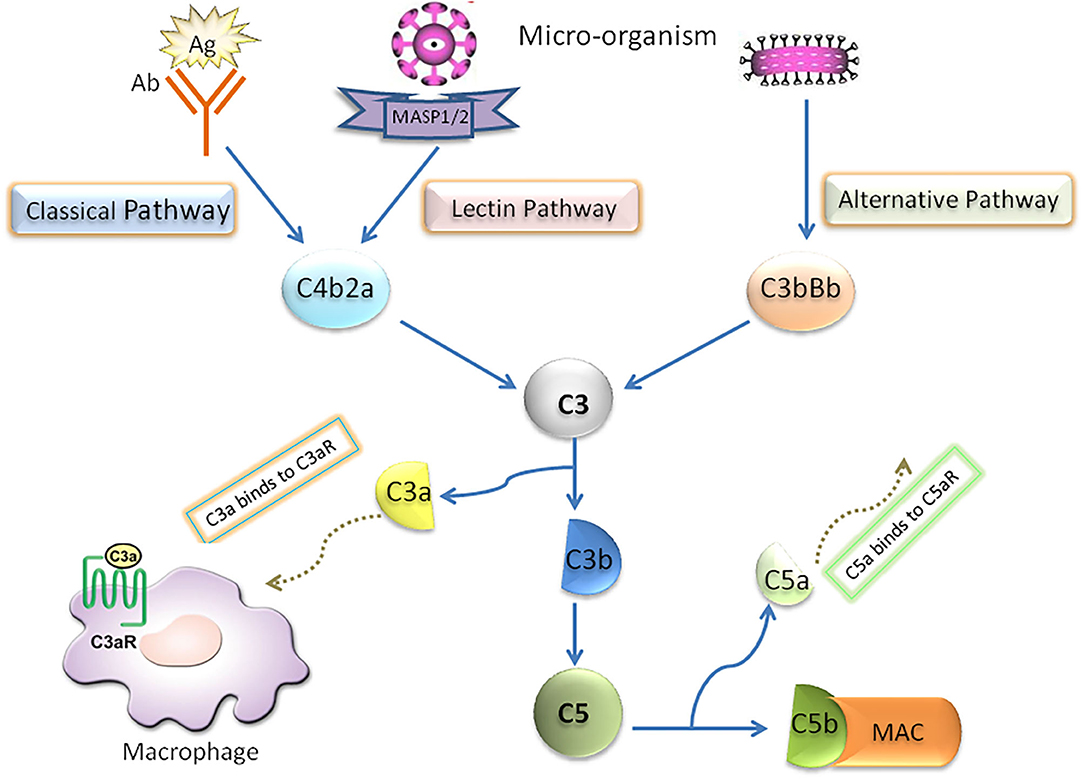
Complement C3 is one of the central components of the complement cascade, a series of enzymatic reactions that can be triggered by various immune triggers, such as the presence of antibodies bound to pathogens or the direct recognition of foreign surfaces. When the complement cascade is activated, C3 is cleaved into two fragments: C3a and C3b.
C3a is a small peptide that has pro-inflammatory properties and can stimulate inflammation in response to infection. It can also attract immune cells to the site of infection.
C3b, on the other hand, is crucial for opsonization and phagocytosis. Opsonization is a process in which pathogens are marked for destruction by immune cells. C3b can coat the surface of a pathogen, making it easier for phagocytic cells, like macrophages and neutrophils, to recognize and engulf the pathogen. Additionally, C3b can participate in the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), which can directly lyse (destroy) certain pathogens.
Complement C3 is an essential component of the innate immune system and plays a vital role in the body’s defense against infections. Dysregulation or deficiencies in complement components like C3 can lead to increased susceptibility to infections and various autoimmune diseases. Therefore, understanding the function of complement C3 and the complement system as a whole is crucial in the fields of immunology and medicine.
Types of Complement C3:
There is one primary type of complement C3, but it can undergo various post-translational modifications and cleavage events, leading to different forms and activation products. Here are some of the important types and products of complement C3:
-
Complement C3 (C3)
: This is the native form of complement C3, synthesized in the liver and circulating in the bloodstream. It plays a central role in the complement cascade, where it can be activated through various pathways, including the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways. -
C3a
: When complement C3 is activated through any of the pathways, it can be cleaved into two fragments, C3a and C3b. C3a is an anaphylatoxin, meaning it can cause inflammation by triggering the release of histamine from mast cells, leading to vasodilation and increased vascular permeability. -
C3b
: This is another cleavage product of complement C3 and is critical for opsonization. C3b can bind to the surface of pathogens and damaged cells, marking them for phagocytosis by immune cells. It also plays a role in the formation of the C5 convertase complex, further amplifying the complement cascade. -
iC3b
: This is an inactivated form of C3b. iC3b is generated when C3b undergoes additional proteolytic cleavage. It has opsonic properties but is less effective at promoting phagocytosis than C3b. -
C3dg and C3d
: These are degradation products of C3b. They are important for immune complex clearance and B cell activation. C3d, in particular, plays a role in enhancing the immune response by binding to complement receptors on B cells. -
C3c
: This is another degradation product of C3b. It is used in clinical laboratory tests to assess complement activity and diagnose complement-related disorders. -
C3 convertase
: This is an enzyme complex formed during the activation of the complement cascade. It cleaves complement C3 into C3a and C3b, initiating a cascade of downstream complement activation events.
Purpose of Complement C3:
The primary purpose of complement C3, along with the rest of the complement system, is to help the immune system recognize and eliminate pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, as well as damaged or abnormal cells. Here are some key functions and purposes of complement C3:
-
Opsonization
: Complement C3 can bind to the surface of pathogens and other foreign invaders, marking them for destruction by phagocytic cells like macrophages and neutrophils. This process is known as opsonization and enhances the efficiency of phagocytosis, making it easier for immune cells to engulf and digest the target. -
Inflammation
: Complement C3 plays a role in triggering inflammation, a critical response of the immune system to infection or tissue damage. It can initiate the release of inflammatory mediators and recruit immune cells to the site of infection or injury, enhancing the body’s defense mechanisms. -
Membrane attack complex (MAC) formation
: Complement C3 is involved in the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), which is a complex of complement proteins that creates pores in the membranes of bacterial cells and certain other pathogens. These pores disrupt the integrity of the pathogen’s cell membrane, leading to cell lysis and death. -
Immune surveillance
: The complement system, including C3, helps in the continuous surveillance of the body for potential threats. It can detect the presence of foreign substances and activate an immune response even before specific antibodies are produced. -
Clearance of immune complexes
: Complement C3 also plays a role in clearing immune complexes from the bloodstream. Immune complexes are formed when antibodies bind to antigens, and complement activation can facilitate their removal, preventing excessive accumulation and potential harm.
Symptoms of Low and High Complement C3:
Here are the symptoms associated with both low and high complement C3 levels:
Low Complement C3:
-
Increased Susceptibility to Infections:
A complement deficiency of C3 can weaken the immune system’s ability to fight off infections, making individuals more prone to bacterial infections, particularly encapsulated bacteria like Streptococcus pneumonia. -
Autoimmune Diseases:
Low complement C3 levels can be associated with autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and glomerulonephritis. Symptoms of these conditions can include joint pain, skin rashes, fatigue, and kidney problems. -
Immune Complex Deposition:
Low C3 levels can lead to an accumulation of immune complexes in the body, which can deposit in various tissues and cause inflammation. This can manifest as joint pain, skin rashes, and kidney problems. -
Swelling:
In some cases, low complement C3 levels can lead to edema or swelling due to increased vascular permeability. -
Kidney Dysfunction:
Complement C3 is involved in maintaining the health of the kidneys. Low levels can lead to kidney dysfunction, which may manifest as proteinuria (protein in the urine), hematuria (blood in the urine), and high blood pressure.
High Complement C3:
-
Inflammatory Conditions:
Elevated complement C3 levels can be associated with various inflammatory conditions, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammatory disorders. -
Autoimmune Diseases:
Some autoimmune diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis and SLE, can lead to increased complement C3 levels as part of the inflammatory response. Symptoms may include joint pain, fatigue, and skin rashes. -
Allergic Reactions:
High complement C3 levels can occur during allergic reactions and anaphylaxis, contributing to the inflammatory response and symptoms like hives, itching, and swelling. -
Liver Disease:
Liver dysfunction can lead to increased complement C3 production, and this can be a marker of liver disease. Symptoms of liver disease may include jaundice, abdominal pain, and changes in appetite. -
Nephrotic Syndrome:
In some cases, elevated complement C3 levels may be associated with nephrotic syndrome, a kidney disorder. Symptoms can include edema, proteinuria, and high cholesterol levels.
Why Do I Need a Complement C3 Test:
Complement C3 is part of the complement system, which is a group of proteins that play a crucial role in your immune system’s ability to fight infections and maintain overall immune function. Here are some reasons why you might need a Complement C3 test:
-
Monitoring Immune Function
: Complement C3 is an important component of the innate immune system. Measuring its levels can help assess the overall activity of this part of your immune system. Doctors may use this test to monitor immune function in certain conditions, such as autoimmune diseases or chronic infections. -
Diagnosing Autoimmune Diseases
: Low levels of complement C3 can be associated with autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis. Elevated levels can also be seen in some autoimmune conditions. A Complement C3 test can be used as part of the diagnostic process for these diseases and to track disease activity. -
Evaluating Inflammatory Conditions
: Complement C3 levels can rise in response to inflammation in the body. Therefore, this test can be used to assess the severity of inflammatory conditions, including but not limited to autoimmune diseases, infections, and certain kidney diseases. -
Monitoring Kidney Function
: The complement system plays a role in kidney function, and abnormal C3 levels can be indicative of kidney problems. Physicians may use this test to help diagnose and monitor conditions like glomerulonephritis, which can affect the kidneys. -
Assessing Response to Treatment
: If you have a condition that affects complement C3 levels, such as lupus, your healthcare provider may use this test to evaluate how well you are responding to treatment. An increase in C3 levels may indicate improvement, while a decrease could suggest a worsening of the condition. -
Research and Clinical Trials
: In some cases, Complement C3 tests are used in clinical research or trials to study the complement system’s role in various diseases and to develop new treatments.
Keep in mind that the interpretation of Complement C3 test results should be done by a healthcare professional who can consider your medical history, symptoms, and other test results.
What Does The Complement C3 Test Result Mean?
The complement C3 test measures the level of complement C3 in your blood. Complement C3 is a protein that plays a crucial role in the body’s immune system, specifically in the complement system. The complement system is a group of proteins that help the immune system recognize and destroy foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses. Complement C3 is one of the central components of this system.
The complement C3 test results can provide important information about your immune system’s function. Here’s what different results might indicate:
-
Normal Range
: If your complement C3 levels fall within the normal range, it typically suggests that your immune system is functioning properly, and there are no significant issues related to complement C3 deficiency or overactivity. -
Low C3 Levels (Hypocomplementemia)
: Low levels of complement C3 can be seen in various medical conditions, including autoimmune diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus), kidney disease (nephrotic syndrome), and some genetic disorders (such as hereditary angioedema). Low C3 levels can indicate an overactive complement system or the consumption of complement proteins due to ongoing inflammation or immune reactions. -
High C3 Levels (Hypercomplementemia)
: Elevated levels of complement C3 can also be associated with certain medical conditions, such as acute infections, inflammatory diseases (like rheumatoid arthritis), or some types of kidney diseases. High C3 levels can indicate an overactive immune response or chronic inflammation.



Buy , Sell Bali Real Estate
Amazing Properties in Bali
The Perfect Place to Live
[…] composition. Additionally, GH can stimulate the uptake of amino acids and their incorporation into proteins, supporting tissue repair and […]
[…] BNP levels within the normal range typically suggest that there is no significant heart dysfunction. […]
[…] the function of immune cells, including macrophages and dendritic cells, which are involved in the immune system‘s response to infection and […]
[…] but they can indicate that further investigation is necessary to determine the underlying cause of inflammation. Monitoring CRP levels can also be useful in assessing the effectiveness of treatments for […]
[…] Neutrophils release elastase, an enzyme that helps break down the structural proteins of bacteria and fungi. […]
[…] perform this test themselves, even in the absence of medical advice, and remember to consult physicians every time they visit them for the rest of their […]
[…] this sensitization, the antigen-antibodies together form a complex and the presence of this complex initiates the sensitization […]
[…] SLE, it is believed that the formation of immune complexes between anti-dsDNA antibodies and DNA can contribute to the inflammation and tissue damage seen in […]
[…] and monitoring various kidney conditions, including chronic kidney disease, acute kidney injury, nephritis, and urinary tract infections. They are also used to assess the impact of medications and […]