Antigen Vs Antibody Difference
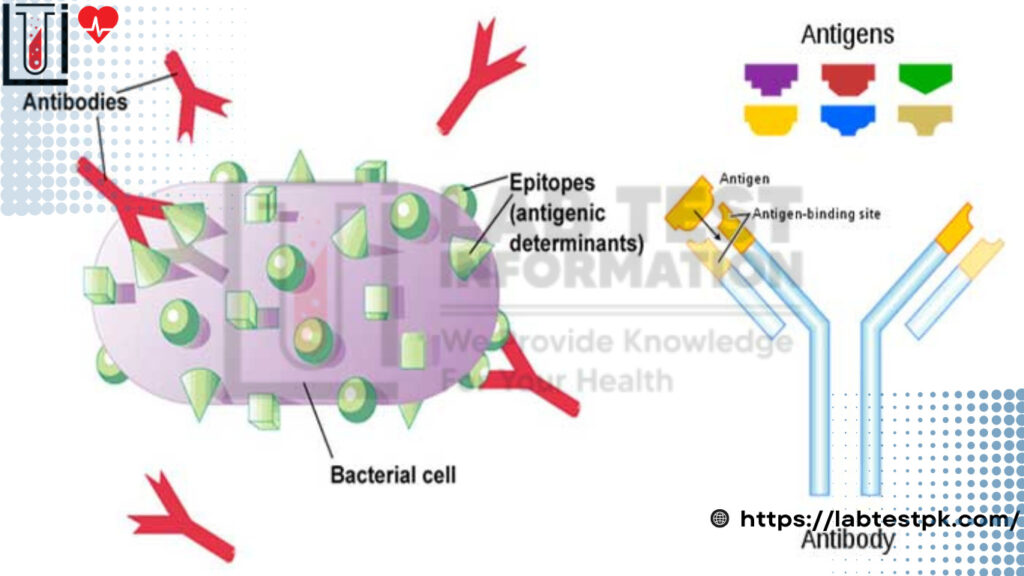
Antigen Vs Antibody Difference, Antigen is any substance that is not related to your body called Not-Self Protein, except for a few antigens belonging to your blood group, which are present on LED blood cells called (self Protein). The antigen can be in any form and enter our body from the external environment in different shapes and sources.
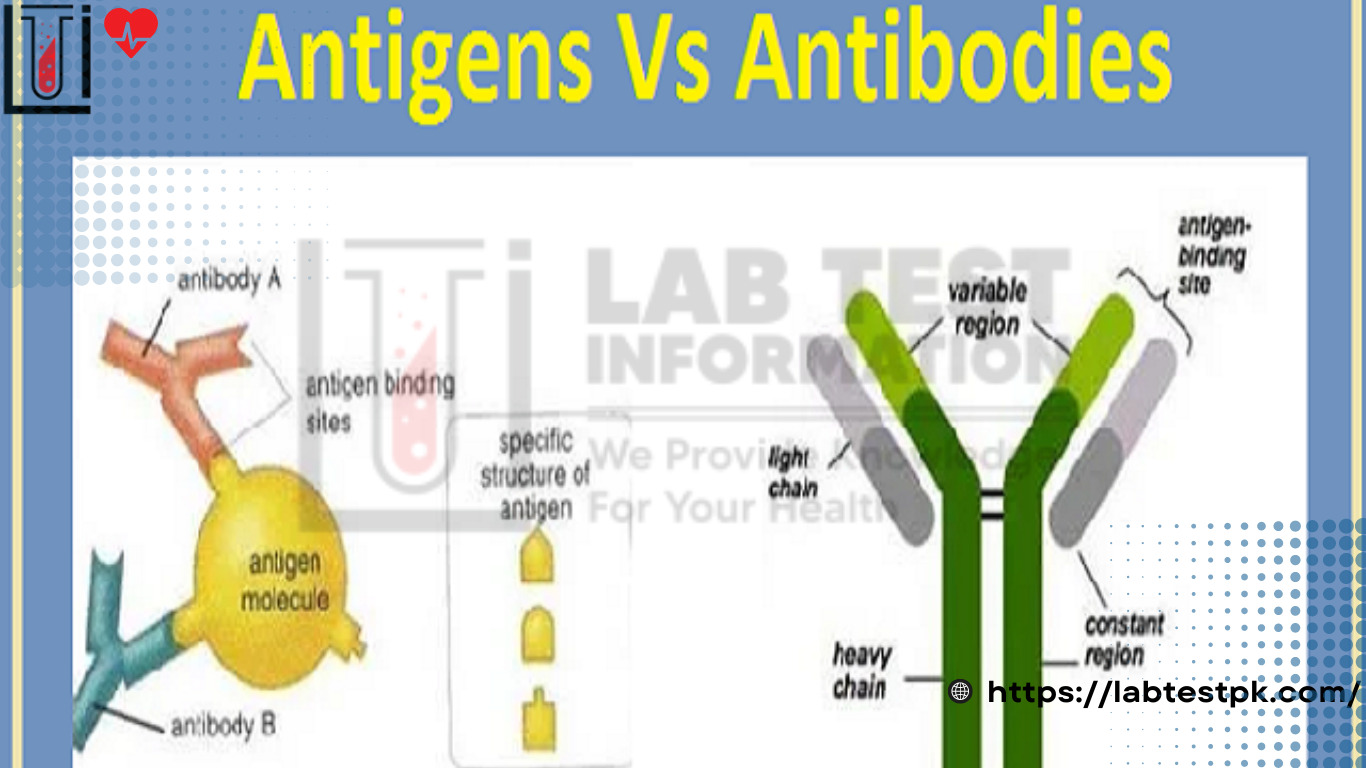
Antibodies are made up of Protein. It is a Protein molecule Produced against antigens. It is found on the surface of plasma cells that Protect the body. Antibodies recognize and latch onto antigens to remove them from the body.
Difference Between Antigen Vs Antibody:
| Antigen | Antibody | |
| Known as | It is also known as Immunogen | It is also known as Immunoglobulins |
| Definition | Substances that can trigger an immune response | The antibody is a protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects (antigens) |
| Examples | Examples of Antigens are Bacteria, viruses, parasites, Fungi, Allergens, Toxins, Certain Proteins in food, etc. | Examples of Antibodies are: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE, |
| Composed of | Antigens may be composed of Proteins Amino Acids Lipids Nucleic And or Polysaccharide |
Antibodies are Composed of Four polypeptide chain Two heavy identical chains Two identical light Chains |
| Origin | Antigens have Origins within the body or externally | All antibodies are Proteins Antibodies always originate within the body |
| Types | The types of Ariligen: Exogenous Endogenous Autoantigens |
Types of Antibody: IgG, IgM IgA, IgD, IgE, |
| Regions | Epitopes are regions of antigen that interact with the antibodies. | Paratopes are regions of antibodies that interact with the antigen. |
| LYmphocyte | T-Lymphocytes Origin: Bone marrow: The cells can mediate immune system (CMIS). Defend against pathogens in our in-cell slow onset It reacts against transplant Cancer cells. |
B-lymphocytes: Whenever an antigen comes into the body from outside, the B-lymphocytes (B-cells) in our body make antibodies to defend our body against these antigens and try hard to eliminate these antigens from the body. |
FAQs:
No 1: What do you mean by Antigen?
A foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body. They are commonly proteins or polysaccharides. They can interact and bind to Ab(specific).
No 2: What do you mean by Antibody?
Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins that are Produced by B cells of the immune system in response to exposure to an antigen.
No 3: What do you mean by immunogen?
An immunogen is a specific type of antigen that is able to exist as an immune response. All immunogens are antigens, but not all antigens are immunogens.
No 4: Types of Immunoglobulin or its Function:
| Types | Function |
| IgI and IgM | Activate the complement System |
| IgE | Involved in allergic responses |
| IgM | Predominant in Primary |
| IgG or IgA, | Has different subtypes |
| IgG, | Can transfer across the Placenta |
No 5: Which Ig is structurally characterized?
Peutametric.
No 6: Which Ig is found or is recreated?
In for mucosal immunity IgA.
MCQs:
Q No. 1: Which of the following medicate Type hypersensitivity reaction or is heat?
Answer:
(a) ✓ IgE
(b) IgD
(c) IgM
(d) IgG
Q No. 2: Anti-Rh antibodies are?
Answer:
(a) ✓ IgG
(b) IgD
(c) IgA
(d) IgM
Q No. 3: Which bonds as forces are involved in the antigen-antibody interaction?
Answer:
(a) Your design works for
(b) Hydrophobic inter-turn
(c) Electrostatic interactions to charged side chain
(d) ✓ Hydrogen bonds
Q No. 4: Which of the following is only contained in the heavy chains or not a leader in light chains?
Answer:
)a) leader
(b) Joining
(c) ✓ Diversity
(d) Variable

[…] IgG and IgM are both antibodies present in the Sample of the patient, It indicates Latent Acute infe… […]
[…] to as red cells, red blood corpuscles, hematomas, erythroid cells, or erythrocytes, are the most common type of blood cells and vertebrates. WBC, white blood cells are part of the body’s immune system. They help the body fight […]
[…] Loss of ketone bodies. […]
[…] from the environment, and they are already exposed to a particular antibiotic in other human body. Sometimes this antibiotic resistance is against a Particular antibiotic, sometimes it is against Some antibiotics and sometimes it can […]
[…] If chronic hepatitis B leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant. […]
[…] IgA antibodies are primarily found in mucosal areas like the digestive tract. They play a crucial role in preventing candida from penetrating the mucosal barrier. […]
[…] RNA is another type of genetic material. It contains information that has been copied from DNA and … […]
[…] High-Grade fever […]
[…] (water-repelling) or hydrophilic (water-attracting) based on the nature of their side chains. Hydrophobic amino acids are typically found in the interior of proteins, while hydrophilic amino acids are […]
[…] This reaction is usually seen in animals with immune-mediated hemolytic anemia. In these, interpretation of incompatible crossmatches is very difficult and a compatible donor may n…. […]
[…] This is a part of flow cytometry that helps identify the specific types of lymphocytes (B-cells or T-cells) involved in the […]
[…] Colon Cancer […]