Anemia Symptoms, Anemia is a condition in which the concentration of red blood cells (erythrocytes) or hemoglobin the oxygen-carrying pigment is below normal. A blood disorder characterized by a decrease in red blood cells, which are primary transporters of oxygen to the body tissues. In this condition, blood does not have enough healthy red blood cells or dysfunctional red blood cells in the body.
Common Types of Anemia
- Iron deficiency Anemia
- Vitamin deficiency Anemia
- Pernicious Anemia
- Aplastic Anemia
- Hemolytic Anemia
- Sickle cell Anemia
- Anemia of Chronic Disease
Iron – deficiency Anemia
The most common type of anemia. Do not have enough iron in your body
Causes can include:
- Gastrointestinal conditions such as ulcers, hemorrhoids, gastritis, and cancer.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)such as aspirin and ibuprofen, can cause ulcers and gastritis
- Women’s period (especially if have menstruation)
- Pregnancy-related anemia
- Iron deficient due to poor absorption
Vitamin-Deficiency Anemia
Low levels
- Vitamin B12
- Folate (folic Acid)
- Poor dietary intake
Pernicious Anemia
- Vitamin B12 cannot absorbed in the GI tract
Aplastic Anemia
- Bone marrow stops making enough blood cells
- Deficiency of blood-forming stem cells in bone marrow
- The body’s immune system attacks the stem cells
- Viral infection
- ionizing radiation
- exposure to toxic chemicals or drugs
Hemolytic Anemia
RBCs are broken up in the bloodstream or spleen
- Mechanical causes
- infections
- Automobiles disorders
- Congenital abnormalities
Sickle Cell Anemia
- Inherited hemolytic anemia
- Hemoglobin protein is abnormal
- RBCs become rigid and clog the circulation
- Unable to flow through small blood vessels
Anemia of Chronic Disease
- Chronic disease can affect the body’s ability to make RBCs
Hormone (erythropoietin)
- Signal bone marrow to make new or more RBCs
Chemotherapy (to treat various cancers)
- Impairs the body’s ability to make new RBCs
Causes of Anemia
- Blood loss: due to any reason will cause anemia if blood loss is in excess amount.
- Inadequate production of red blood cells: if our bone marrow is not able to make enough red blood cells.
- Excessive destruction of red blood cells due to a variety of reasons will cause anemia.
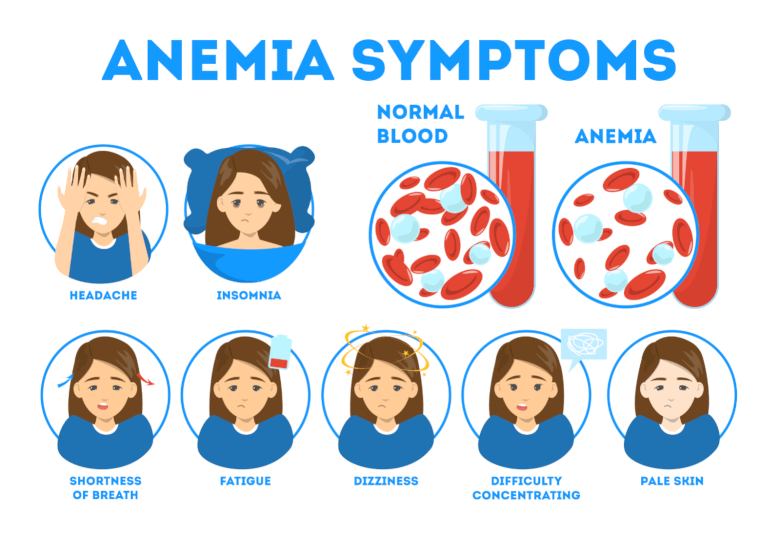
Symptoms of Anemia
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Heart palpitations
- Difficulty in Concentrating
- Chest pain (angina pectoris)
- Headache, cold hands and feet
- Pale yellow skin, chest pain
Each anemia will also exhibit a set of unique symptoms: For example
- Sour of mouth with cracks at the corners in iron deficiency anemia
- People suffering from anemia caused by vit. B12 deficiency
- Hallucination
- Delayed growth and development in children
- Episodes of severe joint Pain
- Abdominal Pain
Risk factors of Anemia
- Prolonged menstruation
- Poor diet
- Genetic Susceptibility
- Pregnancy
- Medicine side effect
- Intestinal disorders
- People on blood thinners
Diagnosis of Anemia
- A complete medical history, a physical examination, and blood tests are all essential to diagnose anemia.
- CBC also called Full body count, is usually performed which determines the number, size, volume, and hemoglobin content of red blood cells.
- Once a diagnosis of anemia is confirmed additional tests are given to ascertain the specific underlying cause.
- The level of blood in iron and the serum levels of ferritin, the principle form in which iron is stored in the body are measured, because these are the best indicators of the body’s total iron stores.
- However, if vitamin deficiency is suspected, then blood levels of vitamins B12 and folate are measured.
- Specific blood is used to detect rare causes of anemia, such as an autoimmune disorder directed against the red blood cells, and red blood cell fragility.
- Hemolytic anemia can be identified by measuring the by-products of red blood cell degradation in the urine and blood.
- In some rare cases, bone marrow may be removed for analysis.
Treatment of Anemia
- Treatment of anemia is cause-specific
- Anemia caused by the deficiency of nutrients such as iron or B12 is treated with long-term supplementation of the depleted nutrient by injection or tablet form.
- Aplastic anemia may be treated by a blood transfusion, a bone marrow transplant, or a course of immunosuppressant drugs to suppress the immune system.
- Currently, there are no treatments for inherited anemias, such as thalassemia and sickle cell anemia, which is caused by the production of abnormal red blood cells.
- The administration of oxygen, pain-relieving drugs, and oral and intravenous, fluids are provided to improve the symptoms.
- Treatment is sometimes with blood transfusion, but regular transfusion can cause a build-up of iron in the body.
- Bone marrow transplant is another possibility.
- Management of hemolytic anemia includes avoiding suspect medications, treating related infections, and taking drugs that suppress the immune system.
- Anemia treatment through Medication, Antibiotic therapy, and surgery



[…] some cases, your healthcare provider may order this test as part of a broader workup to investigate autoimmune disorders. PR3 antibodies can sometimes be elevated in other conditions, so this test can help […]
[…] parameter is used to evaluate the type of anemia and other health conditions like thalassemia, liver disease, cancer, and inherited disease that can […]
[…] plays a crucial role in the regulation of red blood cell production in the body, a process known as erythropoiesis. EPO is essential for maintaining the body’s oxygen-carrying capacity by stimulating the […]
[…] red blood cells are destroyed by the recipient’s immune system. There are two main types of hemolytic transfusion reactions: immune-mediated and […]
[…] of complications related to the abnormal shape of their red blood cells, including pain crises, anemia, and organ […]
[…] “red cell phenotype” typically refers to the characteristics or traits exhibited by red blood cells (RBCs), particularly in the context of blood group systems. Red blood cells play a crucial role in […]
[…] with microangiopathy.Teardrop-shaped cells known as dacrocytes are linked to severe iron deficiency anemia and […]
[…] is a genetic condition that affects red blood cells and can lead to a condition called hemolytic anemia, which is characterized by the premature destruction of red blood […]
[…] important to note that high ferritin levels can also be caused by other conditions, so this test alone is not sufficient for a […]
[…] of metabolism, particularly fatty acid oxidation disorders and organic acidemias. These are rare genetic conditions that affect the body’s ability to break down certain fatty acids or amino acids […]
[…] This parameter is used to diagnose Anemia. […]
[…] Arrhythmia (problem with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat) […]
[…] absorption due to pernicious anemia, an autoimmune condition affecting the stomach […]
[…] hereditary blood condition that results in sickle-shaped red blood cells, which can cause anemia, pain, and other life-threatening […]
[…] methylmalonic acid levels include methylmalonic acidemia, a rare inherited metabolic disorder, and pernicious anemia, which is often caused by a lack of intrinsic factor, a substance needed for the absorption of […]
[…] the presence of antibodies against intrinsic factors. This is often seen in individuals with pernicious anemia or other autoimmune conditions that affect the stomach. A positive result suggests that there is a […]