Platelet count (PLT) is part of the blood that helps the blood clot. Platelet Count is a test to measure how many platelets you have in your blood. They are smaller than red or white blood cells Platelets are colorless blood cells in the body.
Platelets stop bleeding by clumping and forming in blood vessels injuries. There are tens of thousands of platelets in a single drop of blood. A platelet count is a part of a Complete Blood Count (CBC).
How the test performed
A Blood sample is needed.
How to prepare for the test
You do not need to take special steps before the test.
Why Test Performed
Platelets in your blood can be affected by many diseases. Platelets may be counted to monitor or diagnose diseases, or to look for the cause of too much bleeding or clotting.
Normal Platelets
A normal platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 4,00,000 platelets per microliter of blood.
Having more than 4,00,000 platelets is a condition called thrombocytosis; having less than 150,000 is known as thrombocytopenia. You get your platelet number from a routine blood test called a complete blood count (CBC)
Normal Results
A normal platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 4,00,000 Platelets per microliter (mcL) 150 to 400
Normal value ranges may vary slightly. Some labs use different measurements or may test different specimens. Talk to your doctor about your test results.
Abnormal Results Means
The low platelet count is below 150,000 (150 × 109/L). If your platelet count is below 50,000 (50 × 109/L), your risk for bleeding is higher. Even everyday activities can cause bleeding.
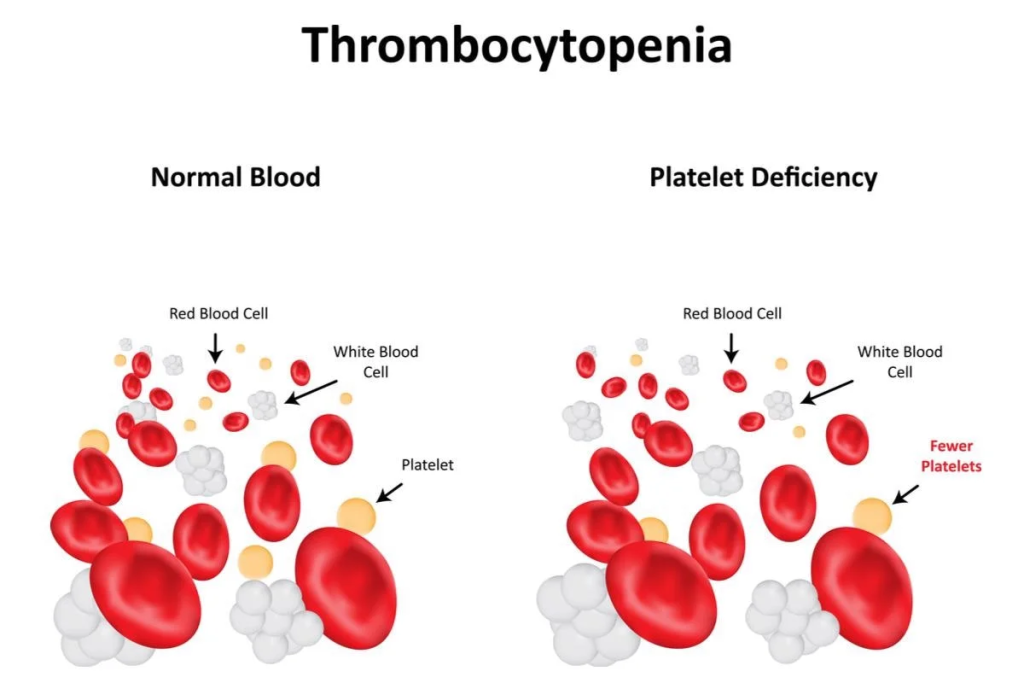
A lower platelet count is called thrombocytopenia.
- Bone marrow being platelets not enough
- Platelets are destroyed in the liver and spleen
- Platelets are destroyed in the bloodstream
Three more common causes of this problem are.
- Drugs and medicines
- Cancer treatment, chemotherapy, and radiation
- Autoimmune disorder,
A high platelet count Plt is more than 4,00,000 called thrombocytosis causes may include
- iron Deficiency
- Cancer
- Certain medicines
- Bone marrow dieses
- After certain medicines
Symptoms
- Bleeding of your gums and nose
- Fatigue
- Blood in urine and stool
- Eczema
- Enlarged spleen
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts
Complications
Dangerous internal bleeding can occur when your platelet count falls below 10,000 platelets per microliter. Though rare, severe thrombocytopenia can cause bleeding into the brain, which can be fatal.


[…] small incisions, punctures, or cuts.Your doctor can choose from a number of tests to evaluate your platelet function. A bleeding time test is a common test to screen patients having prolonged bleeding […]
[…] WBCs(b) Platelets ✓(c) Coagulation factor(d) Mega […]
[…] No. 2: Which of the following Platelet antigens is the receptor for […]
[…] (ET): JAK2 mutations are found in around 50% of ET cases. ET is characterized by an elevated platelet count. When JAK2 mutations are present, they provide additional evidence for the diagnosis of ET, […]
[…] test measures different components of your blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, to check for conditions like anemia, infection, and various blood […]
[…] for platelets Large Cell Ratio. It is a parameter of large platelets in the bloodstream. Large platelets are sometimes called Young platelets and their presence can indicate various underlying conditions […]
[…] platelet volume (MVP) is the average size of your Platelet. When the MPV value is high in blood and platelet count is low, it means that the bone marrow is producing platelets quickly due to increased […]
[…] causes, and it may be due to decreased production, increased destruction, or sequestration of platelets. Some common causes […]
[…] adhesion: It helps platelets adhere to the site of blood vessel […]
[…] ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR): These ratios, calculated from standard blood tests, can serve as […]
[…] RBC(b) Lymphocytes(c) Platelets ✓(d) […]
[…] to develop into various types of blood cells, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These stem cells have several important medical […]
[…] human body is about five percent of the body weight and can increase over time. Red blood cells and platelets are made from special cells in the bone marrow (stem cells). Their different forms. Seen on […]