Understanding Myasthenia Gravis (MG) often involves a combination of tests. A blood test looks for antibodies that attack the junctions between nerves and muscles, a hallmark of MG. This test is highly accurate but may be negative in some cases, particularly early on or if only eye muscles are affected. Electrodiagnostic studies like repetitive nerve stimulation and electromyography (EMG) measure nerve and muscle function. Repetitive stimulation tests for fatigue in muscle response, while EMG assesses electrical activity to identify abnormalities caused by MG. These tests together with a doctor’s evaluation help confirm or rule out MG.
Myasthenia Gravis
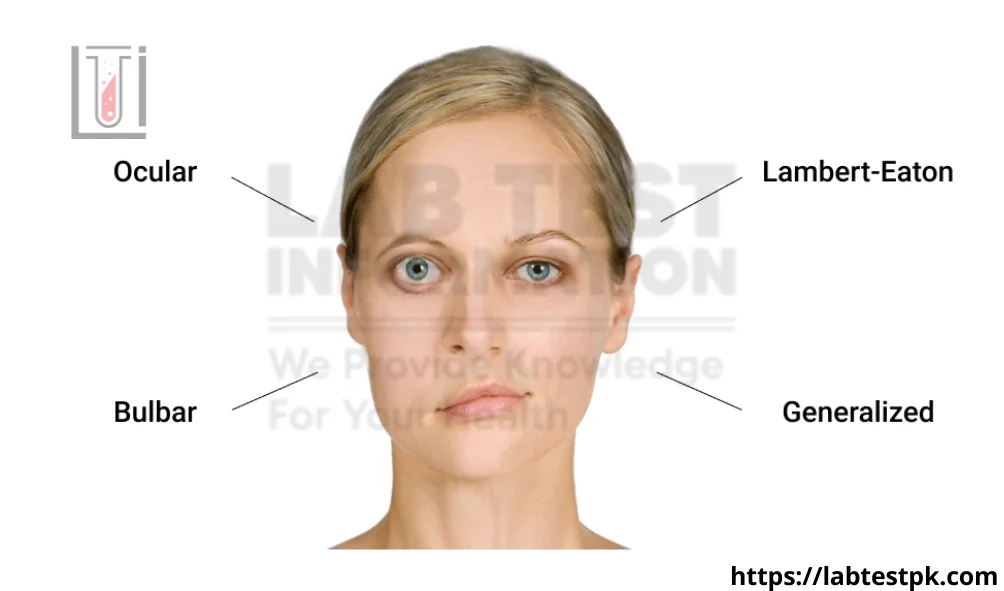
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disorder that causes weakness in the voluntary skeletal muscles, which are your body’s muscles for movement. It mostly affected muscles eyes, face, and swallowing. These antibodies destroy the communication between nerves and muscles, resulting in weakness of the skeletal muscles.
Causes:
- Autoimmune disorders
- Tumor of the thymus
- Deficiency of acetylcholine
- Abnormality in the thyroid gland
Symptoms:
- Breathing difficulty
- Swallowing difficulty
- Impaired speech
- Shortness of breath
- Double vision
- Weakness in legs and hands
- Facial muscle and weakness
- Facial paralysis
- Drooping of eyes lids
- Can not hold the neck
- Respiratory problems may be fatal
Diagnostic Test of Myasthenia gravis:
- History collection
- Physical examination
- Neurological examination
- Ach receptor antibodies test
- CT Scan and MRI scan
- Pulmonary function test
- Edrophonium test
Treatment of Myasthenia gravis:
- No cure MG
- Anticholinesterase drugs
- Immunosupressant (Corticosteriod)
- Oxygen therapy
- Use steroids like Prednisolone given
- Thymectomy


[…] electrical system. This system controls the rate and rhythm of heartbeats. It is called an AV block as the electrical signals that stimulate heart muscle contractions are partially or blocked between […]
[…] autoimmune disease myasthenia gravis is typified by voluntary muscular weakening and exhaustion. By measuring the degree of […]
[…] with trisomy 21 often have distinct facial features, such as a flat facial profile, upward-slanting eyes, a small nose, and a single deep […]
[…] of tissue Through this process, the cells and muscles are preserved in such a way that no changes in their structure occur during chemical factors and […]