Throat Culture Test
Throat Culture Test, A throat culture test also known as a throat swab or throat microbiology culture, is a diagnostic test used to identify the presence of bacteria or fungus in the throat, particularly in the pharynx and tonsils. It is commonly used to diagnose infections or illnesses that affect the throat, such as strep throat (caused by Streptococcus bacteria ) or other bacterial infections.
Symptoms of Throat Culture Test
- Fever
- loss of appetite
- swollen lymph nodes
- Red spots appear on the roof of the mouth
- Tonsils look like red and white spots
Procedure of Throat Culture Test
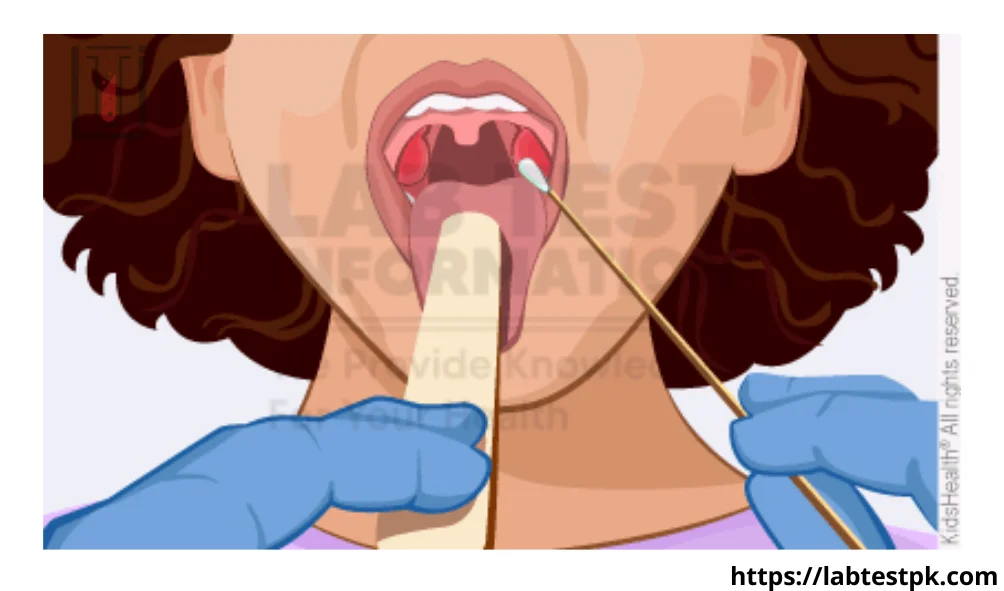
1- A health care provider such as a doctor, or nurse staff, will use a sterile cotton swab to collect a sample from the back of the throat.
2- They often use a tongue depressor to gently hold down the tongue and access the throat more easily.
3- The swab is then carefully inserted into the throat and rubbed against the tonsils or any areas of inflammation or suspected infection.
4- The swab is then placed into a sterile container or transported to a laboratory for analysis.
5- In the laboratory, the collected sample is streaked onto a special growth medium, such as a blood agar plate, to encourage the growth of bacteria if present.
6- This plate is incubated for a specific period, typically 24-48 hours, to allow any bacteria to multiply and form visible colonies.
7- After incubation, microbiologists examine the colonies to identify the type of bacteria and determine whether it is a pathogenic strain.
Diagnosis of Throat Culture
- Gonorrhea
- Thrush
- Whooping cough
- Diphtheria
- Rheumatic fever
Note
The result of a throat test can help diagnose various throat infections, including strep throat and other bacterial infections. It is essential for proper treatment because bacterial infections may require antibiotics. It’s worth noting that throat cultures may be uncomfortable but are usually quick and relatively simple procedures. Rapid strep tests are also available, which provide faster results for diagnosing streptococcal infections, but throat cultures may be performed in cases where the rapid test is inconclusive or to confirm the diagnosis.
FAQs:
- Q: What is a throat culture test?
- A: A throat culture test is a diagnostic procedure where a sample is collected from the back of the throat using a swab. The sample is then cultured to identify the presence of bacteria or viruses.
- Q: Why is a throat culture done?
- A: Throat cultures are typically done to identify the cause of a sore throat, especially to distinguish between bacterial infections like strep throat and viral infections.
- Q: How is the test performed?
- A: A healthcare provider uses a sterile swab to collect a sample from the back of the throat. The swab is then sent to a laboratory for culture and analysis.
- Q: Is the test painful?
- A: The test may cause slight discomfort or a gagging sensation, but it is generally not considered painful.
- Q: How long does it take to get results?
- A: Results can vary, but they are typically available within 24 to 48 hours after the sample reaches the laboratory.
- Q: What does a positive result mean?
- A: A positive result indicates the presence of bacteria, most commonly Group A Streptococcus, which causes strep throat. It helps guide appropriate antibiotic treatment.
- Q: What does a negative result mean?
- A: A negative result suggests that bacteria were not detected in the throat culture. However, it does not rule out other causes of a sore throat, such as viral infections.
- Q: Are there any risks associated with the test?
- A: Throat culture tests are generally safe with minimal risks. The discomfort during the swabbing is usually temporary.
- Q: Can the test detect viruses?
- A: Throat culture tests are primarily designed to identify bacterial infections. Viral infections may not be detected by this method, and other tests may be needed.
- Q: Can antibiotics be prescribed without a throat culture?
- A: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe antibiotics based on symptoms and clinical evaluation. However, a throat culture is recommended to confirm bacterial infection and guide appropriate treatment.

[…] O is a toxin Produced by group A Streptococcus. The main bacteria in group A Streptococcus is (Streptococcus Pyogenese). The infection is caused […]
[…] Sore throat […]
[…] the most common form of color blindness is red-green color blindness. Where people are unable to distinguish between different shades of red and […]
[…] Agar is a gelatinous substance derived from seaweed. It serves as the solidifying agent for the medium, […]
[…] throat: Severe sore throat may resemble strep throat but doesn’t improve with […]