Microscope uses
Microscope uses, The microscope is one of the most important equipment used in a laboratory. A laboratory is incomplete without a microscope. Its safety and maintenance after use are very important.
How does a microscope work?
A microscope magnifies small objects. It works through the lens and the light, for which a certain distance between the light and the lens is necessary. The microscope has special knobs for this particular distance. The lower gear of the microscope is called the objective and the upper one is called the eyepiece.
The Ability to Magnify Objects in a Microscope:
| (Total Magnification) | (Eye Piece Magnification) | (Objective Magnification) |
| 100 | 10x | 10x |
| 400 | 10x | 40x |
| 1000 | 10x | 100x |
Note:
To see an object under a microscope, first focus on a low magnification. Use objective magnification to go into more detail. Eyepiece magnification remains constant.

Oil Immersion:
The oil emission technique is used for a more detailed study of small objects. Focus the subject on the normal lens first before going into it.
Light management in the microscope:
Special light bulbs are installed in the stand under the microscope. The light emitted from them does not spread too far and there are condensers for control. Special tungsten or halogen bulbs are used for illumination in the microscope.
Filter:
Filters in the light path perform the following functions:
- Increase or decrease the amount of light.
- Reduce or increase the ability to see things under a microscope.
- Reducing harmful effects on eyes from ultraviolet rays emitted by light bulbs.
Mechanical Stage:
In this part of the microscope, the observation slide is clamped so that the slide does not move around during observation and the object under observation can be seen well. The slide angle on the mechanical stage can be moved not only left and right but also back and forth.
Focusing control:
2 knobs are used for this:
Large Knob:
Can move the mechanical stage up and down quickly.
Fine Focusing Knob:
The Fine focusing tab very gently moves the focused area up or down.
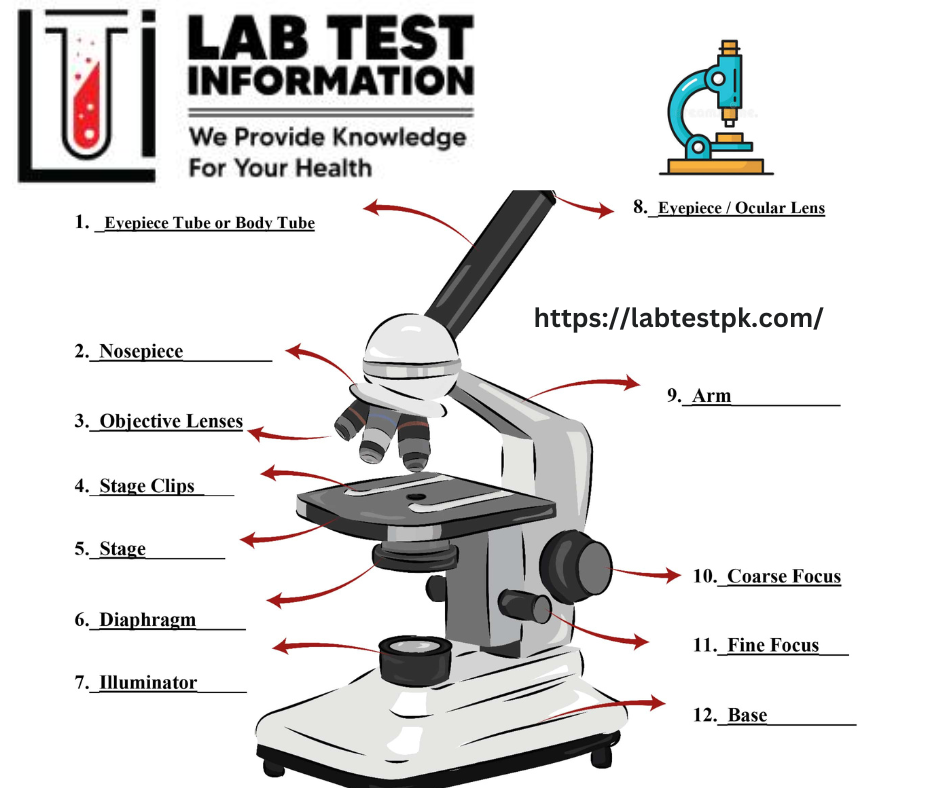
Identify the different Parts of a Microscope:
Before using the microscope, the following parts must be identified:
- Eyepiece
- Rotating lenses
- Mechanical stage and slide holder
- Condenser diaphragm iris
- Focusing knobs small and large
- Bulbs for light
- Bulb dimming control
- Microscope On/Off button
Use of microscope:
- Applying the switch of the microscope to the eyelid
- Dimming the light from the bulb
- Rotate the 10x lens to the focus position
- Fixing a prepared slide stage for observation in a microscope
- Focusing on the specimen and viewing through the eyepiece by rotating the large focusing knob
- Rotate the small knob to get a better look at the sample
- When the specimen is well-focused, rotate the slide back and forth and view the entire scene
- For more detailed observation, use the x 40x 1000 lens and see details through oil immersion.
- To remove the slide from the stage, rotate the 40 × 100x lens to 10x and then remove the slide. Otherwise, the slide will collide with the lens and break or the lens will be damaged
- Clean the leaking oil well with filter paper
Care of the Microscope:
- Learn how to use a microscope correctly.
- Cleanse thoroughly before and after daily use
- Contact your lab engineer immediately in case of difficulty.
- Keep the microscope in a safe and flat place after use.
- Use tissue paper or a soft cloth to clean the microscope lens. Hard cloth can scratch the lens.
- Do not apply force at any stage during use.
- Before closing the microscope, remove the slide and adjust the stage to normal position using the knob.
- The stage can be cleaned with 70% ethanol.
- Cover the microscope with a dust cover.
- Always use both hands to lift the microscope.

[…] received in this department are prepared for microscopic examination. This section covers all the steps involved from specimen collection to preparationthe of stained […]
[…] attached to the fungus dissolves and can be seen. If a group of hyphen ortho spores is seen on microscopic examination, the result is fixative. Enpothrix inside the hair and Ectothrix outside the […]
[…] The virus is visible only under an Electron microscope. […]
[…] of single cells from bodily fluids or tissues. It examines the cells in the fluid tissue under a microscope and checks certain abnormalities in cells. This test is completely different from the […]
[…] small particles or germs that cannot be seen directly with the naked eye, Such a device is called a microscope. It is urgently needed in various medical […]