D-dimer tests are used to check for blood clotting problems. A blood clot can cause health problems. A D-Dimer test looks for D-dimer in blood D-dimer is a protein fragment (small piece) that is made when a blood clot dissolves in your body. A blood clot is important that prevent you from losing too much blood when you are injured, normally blood will dissolve the clot once an injury has healed. Sometimes the conditions may be very serious and even may cause death. Sometimes they injure vessels, arteries, etc.
D-Dimer Test
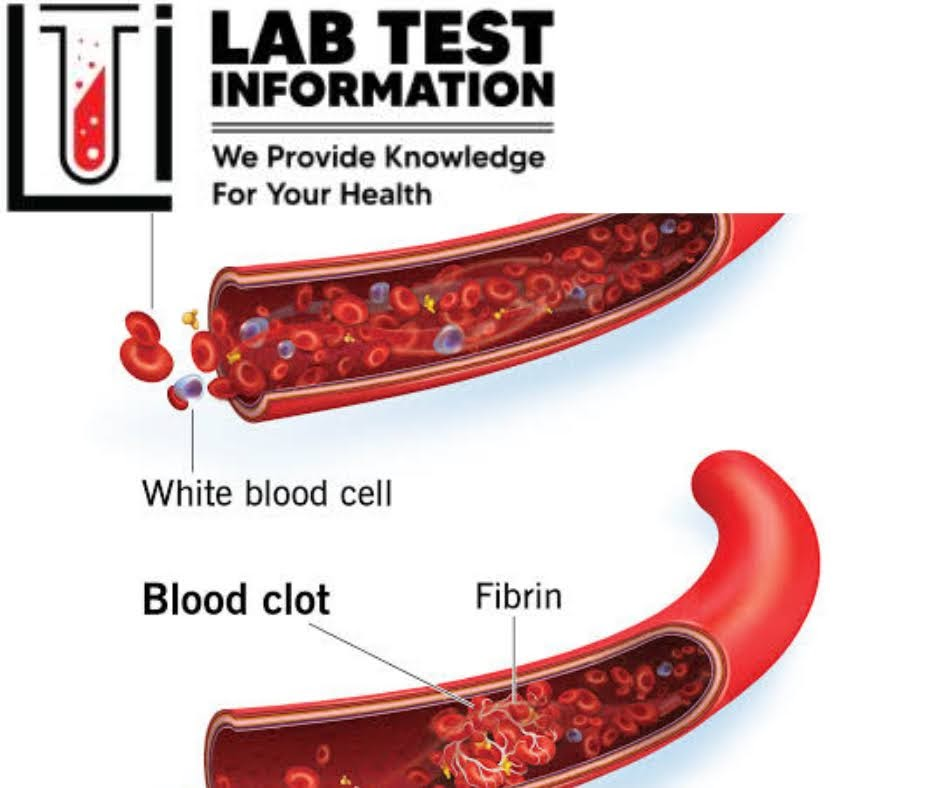
Platelets immediately adhere to the cut edges of the vessels and release chemicals to attract even more platelets. A platelet plug is formed and the external bleeding stops. Next small molecules called clotting factors cause stands of blood bone materials called fibrin to stick together and sit inside of the wound. The cut blood clot dissolves. After a few days, plasmin is an enzyme breakdown.
The clot for removal. The broken fibrin fragments are termed fibrin Degradation products (FDPs). One of the fibrin degradation products D-Dimer normally undetectable in the blood. If present for a long time and not dissolved it will make a thrombus and will lead to embelin also. Due to blood clots, blood circulation will be affected and the supply of oxygen will be affected because of blood Clots in the vessels.
How The Test Performed:
A Blood Sample Needed. Plasma (Sodium Citrate).
Presence of Fibrin Degradation:
- Blood vessels
- In Arteries
- In Veins
Causes Of D-Dimer Test:
Hight D- Dimes Test (>0.5 u/mL)
- Deep Vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Pulmonary embolism (PE)
- Stroke
- Covid-19 infection
False Positive:
- Trauma
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Thrombosis
- Embolism
- Advanced age
- Pregnancy‘s Surgery
- Heart disease
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reference Range of D-Dimer Test:
- Less than 0.4 mcg/mL
- Less than 250 ng/ml
Cause of Increase D-Dimer Test:
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Symptoms:
- Leg pain or tenderness
- Leg Swelling
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Symptoms:
- Trouble breathing
- Cough
- Chest pain
- Rapid heat beat
- DIC (Disseminated intravascular Coagulation) formation of a clot in where the body
- Renal failure
- Liver failure
- Dengue
- Malignancies (Like Cancer)
Procedure:
Take a blood sample in sodium citrated vail, and centrifuge the sample, then use the FDP kit. FDP kit has the following variables,
- Latex Reagent
- Positive Control
- Negative Control
- Sample
- Take a Petri slide that has 5 to 6 circles.
- Now, Add the 3 drops of latex reagent first 3 circles.
- Then put 1 drop of positive control and the first circle and put negative control on the second circle.
- After the process the put one drop of serum on the third circle.
- Start the stopwatch for 3 minutes and rotate the slide until the end of the time.
- After completing the process you can check the result.

Result Interpretation:
Agglutination in the Sample of the agglutination shows the result is Positive. Results above 250ng/ml and more than 0.4mcg/ml will be Considered abnormal and will indicate blood clots in the blood vessels.
Treatment OF D-Dimer:
- Anticoagulants
- Thrombolytics
- Thrombectomy


very easy wording.most informative lecture ۔ may ALLAH success you in every field of life
[…] in which the body is incapable to take sugar molecules. Energy flows in the body through certain molecules, which creates the body to work correctly. In contrast, obesity also has traits of sugar disease. […]
[…] in which the body is incapable to take sugar molecules. Energy flows in the body through certain molecules, which creates the body to work correctly. In contrast, obesity also has traits of sugar disease. […]
[…] the body’s small blood vessels, leading to excessive bleeding and clotting. Elevated D-dimer levels can be a sign of […]